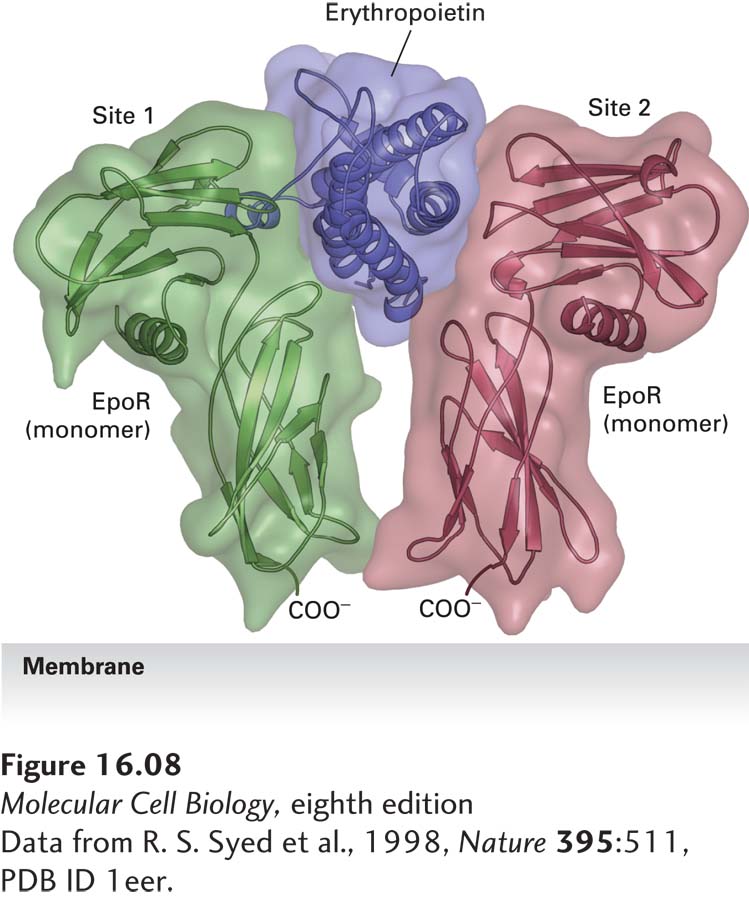
FIGURE 16- 8 Structure of erythropoietin bound to an erythropoietin receptor. Like other cytokines, erythropoietin (Epo) contains four conserved long α helices that are folded in a particular arrangement. The activated erythropoietin receptor (EpoR) is a dimer of identical subunits; the extracellular domain of each monomer is constructed of two subdomains, each containing seven conserved β strands folded in a characteristic fashion. Side chains of residues on two of the α helices in Epo, termed site 1, contact loops on one EpoR monomer, while residues on the two other Epo α helices, termed site 2, bind to the same loop segments in a second receptor monomer, thereby stabilizing the dimeric receptor in a specific conformation.
[Data from R. S. Syed et al., 1998, Nature 395:511, PDB ID 1eer.]
[Leave] [Close]