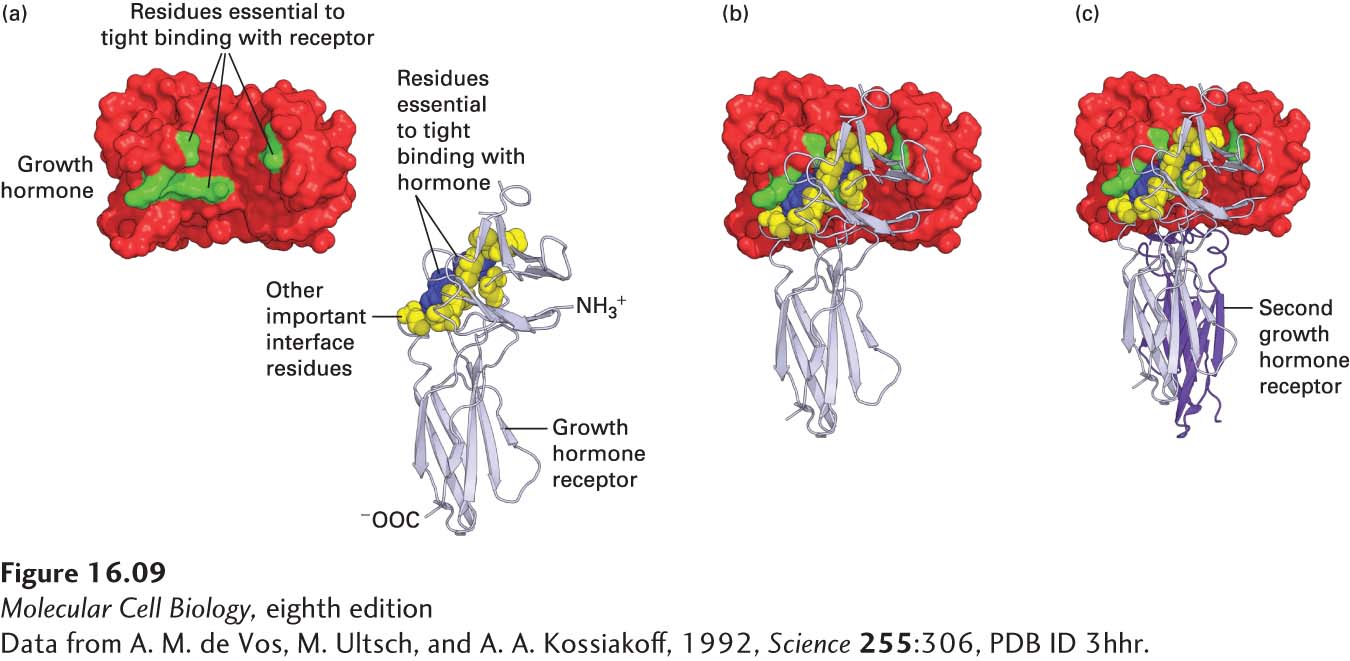
EXPERIMENTAL FIGURE 16- 9 Growth hormone binds to its receptor through multiple weak, noncovalent forces. (a) As determined from the three- dimensional structure of the 1 growth hormone:2 growth hormone receptor complex, 28 amino acids in the hormone are at the binding interface with one receptor molecule. To determine which amino acids are important in ligand- receptor binding, researchers mutated each of these amino acids, one at a time, to alanine and measured the effect on receptor binding. From this study, it was found that only 8 amino acids on growth hormone (green) contribute 85 percent of the energy that is responsible for tight receptor binding; these amino acids are distant from one another in the primary sequence, but adjacent in the folded protein. Similar studies showed that two tryptophan residues (blue) in the receptor contribute most of the energy responsible for tight binding of growth hormone, although other amino acids at the interface with the hormone (yellow) are also important. (b) As with the Epo receptor, binding of growth hormone to one receptor molecule is followed by (c) binding of a second receptor (purple) to the opposite side of the hormone; this binding involves the same set of yellow and blue amino acids on the receptor, but different residues on the hormone. See B. Cunningham and J. Wells, 1993, J. Mol. Biol. 234:554, and T. Clackson and J. Wells, 1995, Science 267:383.
[Data from A. M. de Vos, M. Ultsch, and A. A. Kossiakoff, 1992, Science 255:306, PDB ID 3hhr.]
[Leave] [Close]