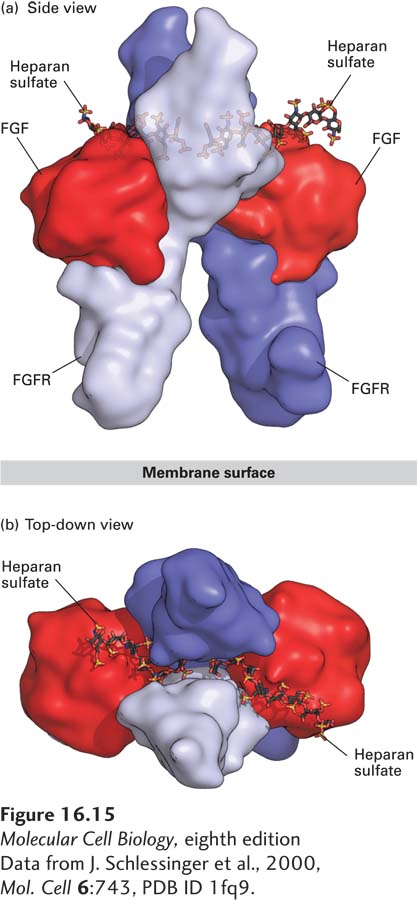
FIGURE 16- 15 Structure of the extracellular domains of the active dimeric fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor, stabilized by binding of two ligands and by heparan sulfate. Shown here are side and top- down views of the complex comprising the extracellular domains of two FGF receptor (FGFR) monomers (purple and violet), two bound FGF molecules (red), and two short heparan sulfate chains, which bind tightly to FGF. (a) In the side view, the upper domain of one receptor monomer (purple) is seen situated behind that of the other (violet); the plane of the plasma membrane is at the bottom. A small segment of the extracellular domain whose structure is not known connects to the membrane- spanning α-helical segment of each of the two receptor monomers (not shown) that protrude downward into the membrane. (b) In the top view, the heparan sulfate chains are seen threading between and making numerous contacts with the upper domains of both receptor monomers. These interactions promote binding of the ligand to the receptor and receptor dimerization.
[Data from J. Schlessinger et al., 2000, Mol. Cell 6:743, PDB ID 1fq9.]
[Leave] [Close]