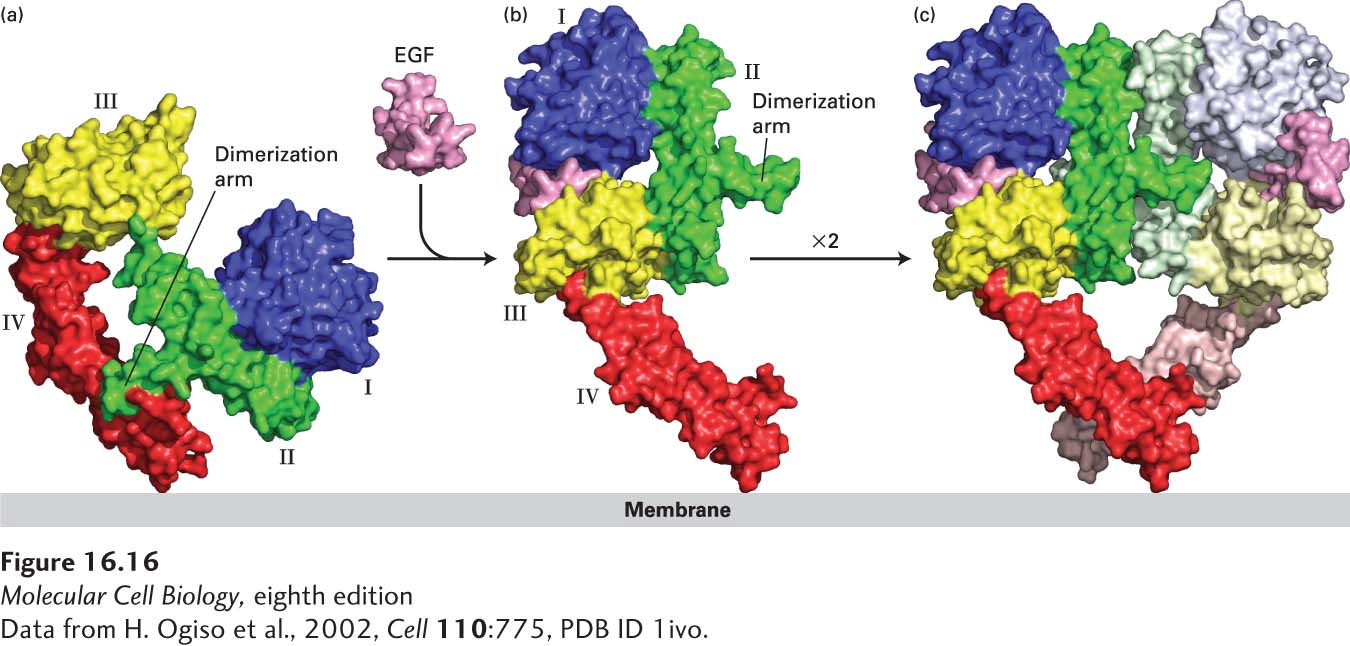
FIGURE 16- 16 Ligand- induced dimerization of HER1, a human receptor for epidermal growth factor (EGF). (a) The extracellular region of all EGF receptors contains four domains: domains I (blue) and III (yellow) are closely related in sequence, as are domains II (green) and IV (red). In the absence of bound EGF, the receptor is mostly monomeric and the intracellular kinase is inactive. The extracellular region adopts a configuration in which the β-hairpin from domain II that forms the “dimerization arm” binds to domain IV of the same receptor molecule. (b) EGF binds simultaneously to domains I and III; binding induces a major conformational change in the extracellular domain such that the dimerization arm of domain II is now exposed. (c) Dimerization of two identical ligand- bound receptor monomers in the plane of the membrane occurs primarily through interactions between the dimerization arms of the two receptors.
[Data from H. Ogiso et al., 2002, Cell 110:775, PDB ID 1ivo.]
[Leave] [Close]