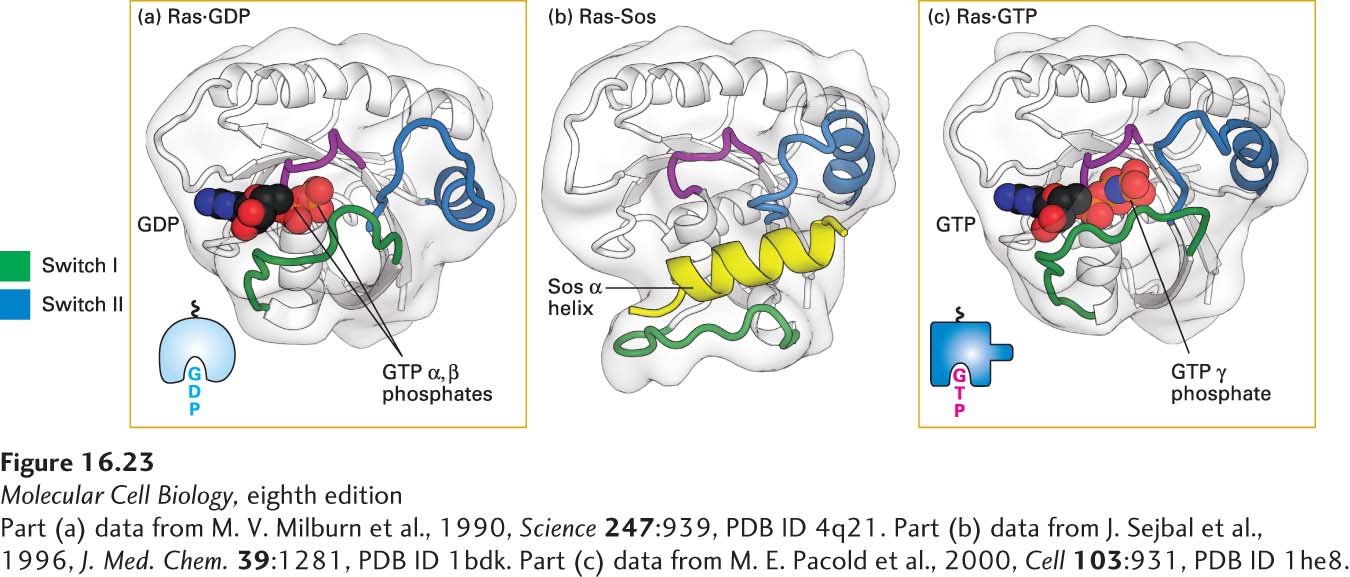
FIGURE 16- 23 Structures of Ras bound to GDP, Sos protein, and GTP. (a) As with other G proteins bound to GDP, in Ras·GDP, the switch I (green) and switch II (blue) segments do not directly interact with GDP. (b) One α helix (yellow) in Sos binds to both switch segments of Ras·GDP, leading to a massive conformational change in Ras. In effect, Sos pries Ras open by displacing the switch I region, thereby allowing GDP to diffuse out. (c) GTP is thought to bind to the Ras- Sos complex first through its base (guanine); subsequent binding of the GTP phosphates completes the interaction. The resulting conformational change in the switch I and switch II segments of Ras, allowing both to bind to the GTP γ phosphate, displaces Sos and promotes interaction of Ras·GTP with its effectors (discussed later). Colored purple is the P loop, a sequence motif found in many ATP- and GTP- binding proteins, which binds the β phosphate of the nucleotide. See Figure 15- 5 for another depiction of Ras·GDP and Ras·GTP.
[Part (a) data from M. V. Milburn et al., 1990, Science 247:939, PDB ID 4q21. Part (b) data from J. Sejbal et al., 1996, J. Med. Chem. 39:1281, PDB ID 1bdk. Part (c) data from M. E. Pacold et al., 2000, Cell 103:931, PDB ID 1he8.]
[Leave] [Close]