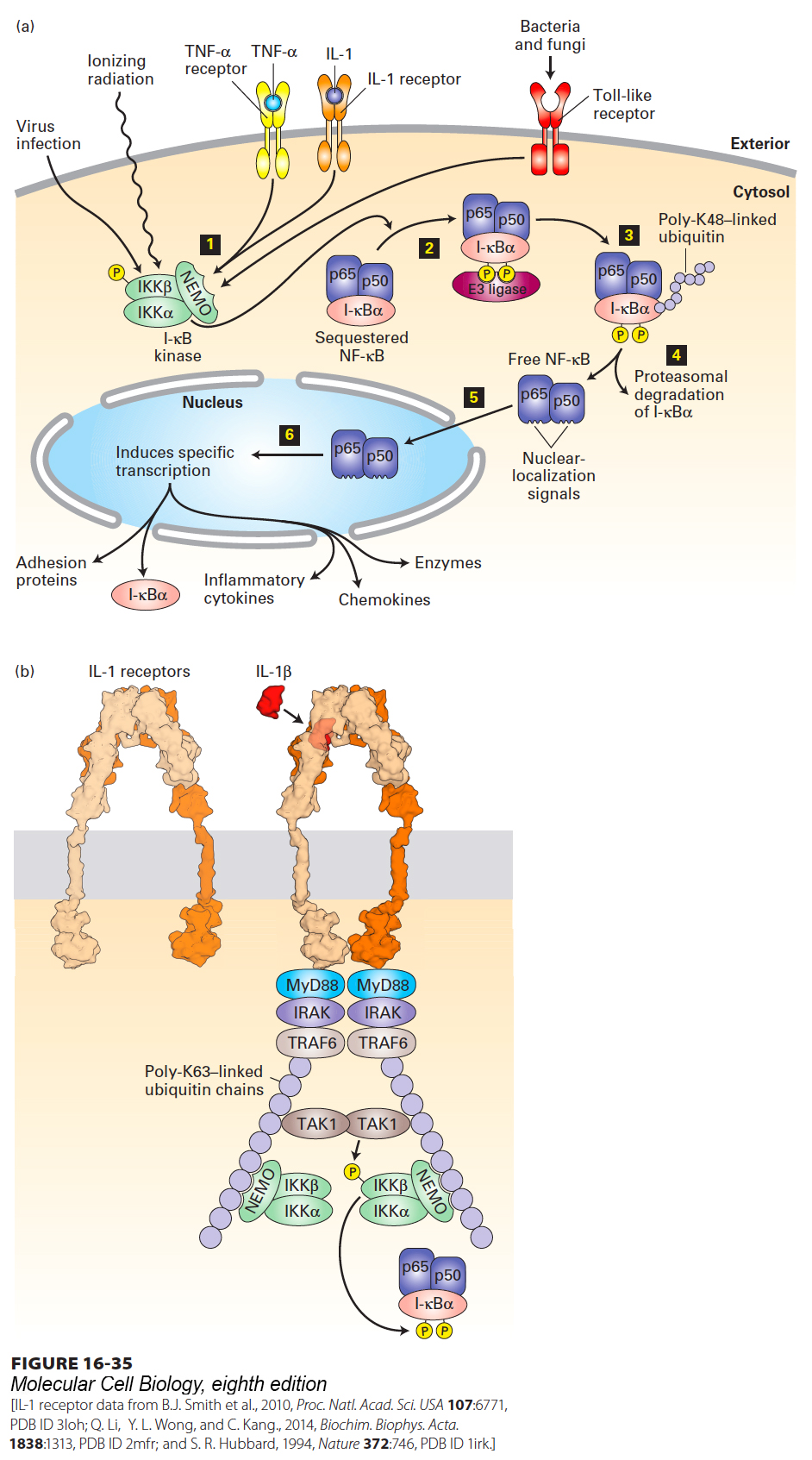
FIGURE 16- 35 Activation of the NF- κB signaling pathway. (a) In resting cells, the dimeric transcription factor NF- κB, composed of p50 and p65 subunits, is sequestered in the cytosol, bound to the inhibitor I- κBα. Step 1: Activation of the trimeric I- κB kinase is stimulated by many agents, including viral infection, ionizing radiation, binding of the pro- inflammatory cytokines TNFα or IL- 1 to their respective receptors, or activation of any of several Toll- like receptors by components of invading bacteria or fungi. Step 2: The β subunit of I- κB kinase then phosphorylates the inhibitor I- κBα, which then binds an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Steps 3 and 4: Subsequent lysine 48– linked polyubiquitinylation of I- κBα targets it for degradation by proteasomes. Step 5: The removal of I- κBα unmasks the nuclear- localization signals in both subunits of NF- κB, allowing their translocation to the nucleus. Step 6: In the nucleus, NF- κB activates transcription of numerous target genes, including the gene encoding I- κBα, which acts to terminate signaling, and genes encoding various inflammatory cytokines. See R. Khush et al., 2001, Trends Immunol. 22:260, and J- L Luo et al., 2005, J. Clin. Invest. 115:2625. (b) Binding of interleukin- 1β (IL- 1β) to heterodimeric IL- 1 receptors triggers receptor oligomerization and recruitment of several proteins to the receptor cytosolic domain, including TRAF6, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, which catalyzes synthesis of long lysine- 63- linked polyubiquitin chains linked to TRAF6, NEMO, and other proteins in the complex. The polyubiquitin chains function as a scaffold to recruit the kinase TAK1 and the NEMO subunit of the trimeric I- κB kinase complex. TAK1 then phosphorylates itself and the β subunit of I- κB kinase, activating its kinase activity and enabling it to phosphorylate I- κBα. See B. Skaug et al., 2009, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 78:769, and J. Napetschnig and H. Wu, 2013 Annu. Rev. Biophys. 42:443.
[IL- 1 receptor data from B.J. Smith et al., 2010, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107:6771, PDB ID 3loh; Q. Li, Y. L. Wong, and C. Kang., 2014, Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1838:1313, PDB ID 2mfr; and S. R. Hubbard, 1994, Nature 372:746, PDB ID 1irk.]
[Leave] [Close]