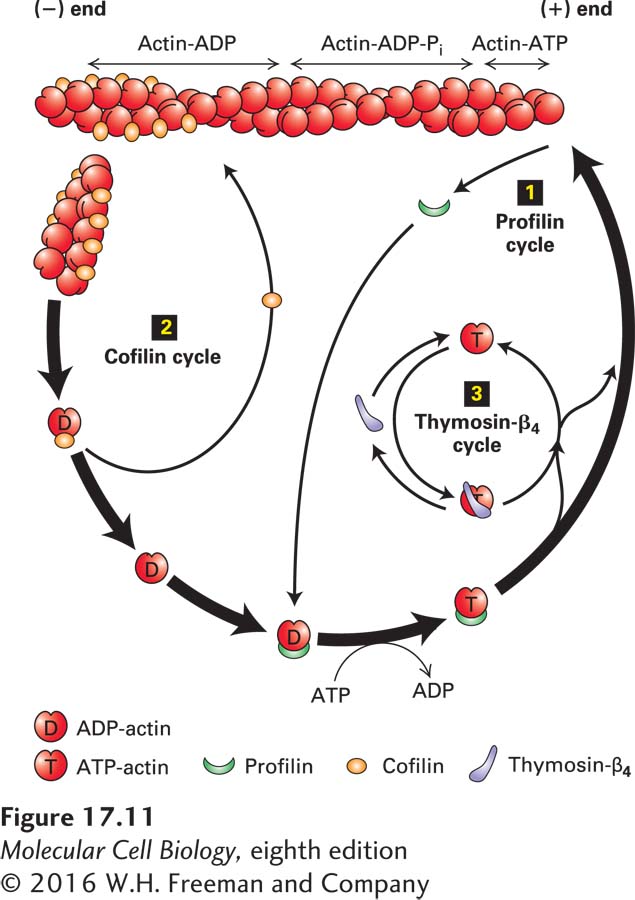
FIGURE 17- 11 Regulation of filament turnover by actin- binding proteins. Actin- binding proteins regulate the rate of assembly and disassembly of actin filaments as well as the availability of G- actin for polymerization. In the profilin cycle 1, profilin binds ADP– G- actin and catalyzes the exchange of ADP for ATP. The ATP– G- actin– profilin complex can deliver actin to the (+) end of a filament with dissociation and recycling of profilin. In the cofilin cycle 2, cofilin binds preferentially to filaments containing ADP- actin, inducing them to fragment and thus enhancing depolymerization by making more filament ends. In the thymosin- β4 cycle 3, ATP– G- actin made available by the profilin cycle is bound by thymosin- β4, which sequesters it from polymerization. As the free G- actin concentration is lowered by polymerization, G- actin– thymosin- β4 dissociates to make free G- actin available for association with profilin and further polymerization.
[Leave] [Close]