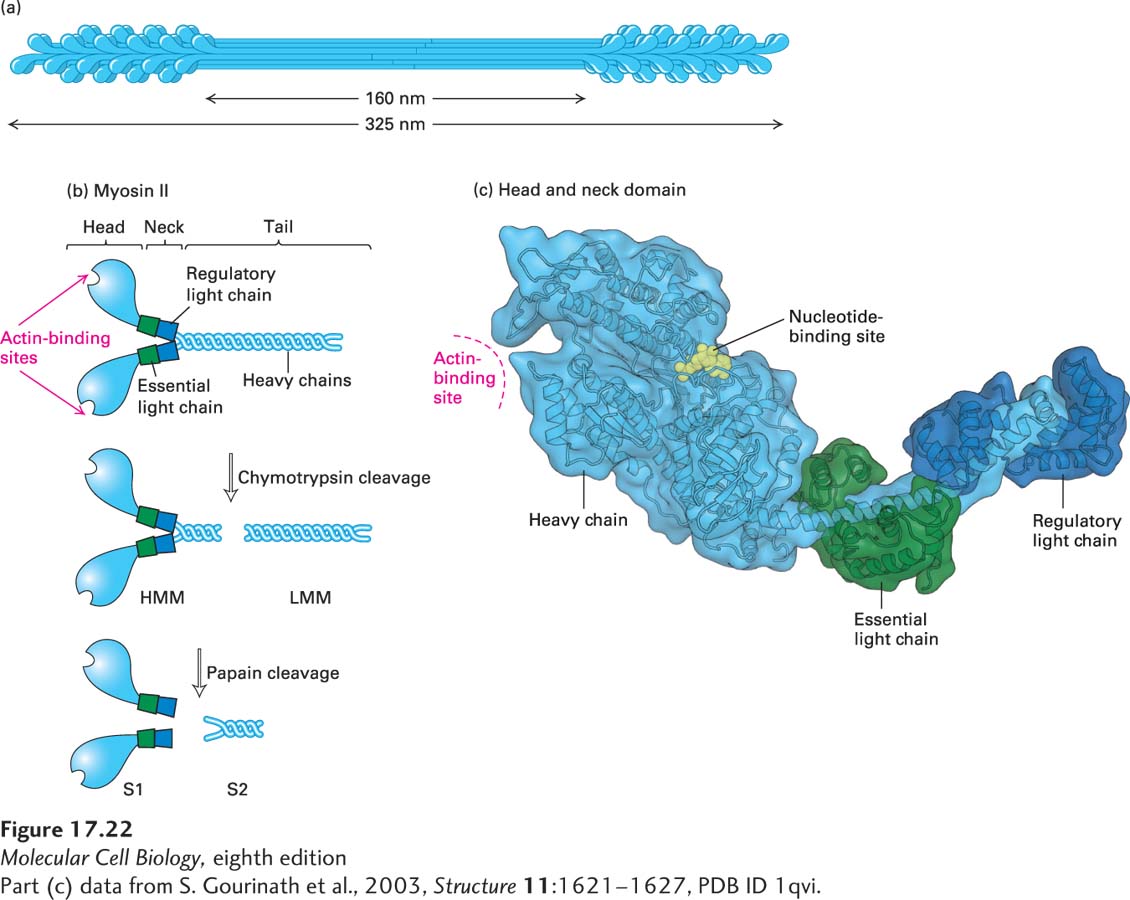
FIGURE 17- 22 Structure of myosin II. (a) Organization of myosin II in filaments isolated from skeletal muscle. Myosin II assembles into bipolar filaments in which the tails form the shaft of the filament and the heads are exposed at the ends. Treatment of bipolar filaments with high salt concentrations and ATP disassembles the filament into individual myosin II molecules. (b) A myosin II molecule consists of two identical heavy chains (light blue) and four light chains (green and dark blue). The tails of the heavy chains form a coiled coil to dimerize; the neck region of each heavy chain has two light chains associated with it. Limited proteolytic cleavage of myosin II generates tail fragments— LMM and S2— and the S1 motor domain. (c) Three- dimensional model of a single S1 head domain shows that it has a curved, elongated shape and is bisected by a cleft. The nucleotide- binding pocket lies on one side of this cleft, and the actin- binding site lies on the other side near the tip of the head. Wrapped around the shaft of the α-helical neck are two light chains. These chains stiffen the neck so that it can act as a lever arm for the head. Shown here is the ADP- bound conformation.
[Part (c) data from S. Gourinath et al., 2003, Structure 11:1621– 1627, PDB ID 1qvi.]
[Leave] [Close]