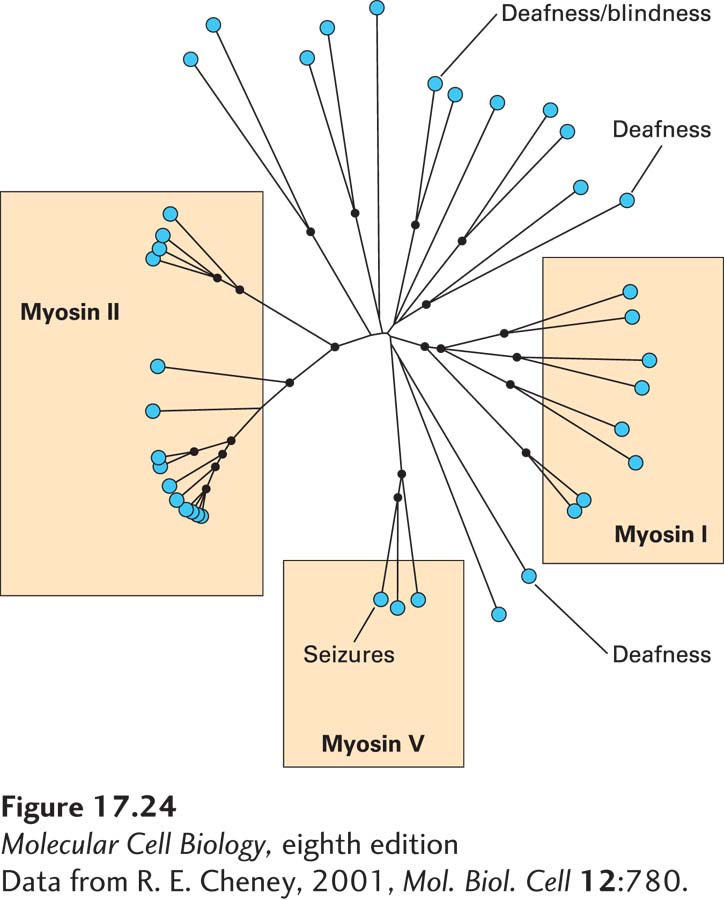
FIGURE 17- 24 The myosin superfamily in humans. Results of a computer analysis of the relatedness of the S1 head domains of all of the approximately 40 myosins encoded by the human genome. Each myosin is indicated by a blue dot. The lengths of the black lines indicate phylogenetic distance relationships: myosins connected by short lines are closely related, whereas those separated by longer lines are more distantly related. Among these myosins, three classes— myosins I, II, and V— are widely represented among eukaryotes; others have more specialized functions. Indicated are examples in which loss of a specific myosin causes a disease.
[Data from R. E. Cheney, 2001, Mol. Biol. Cell 12:780.]
[Leave] [Close]