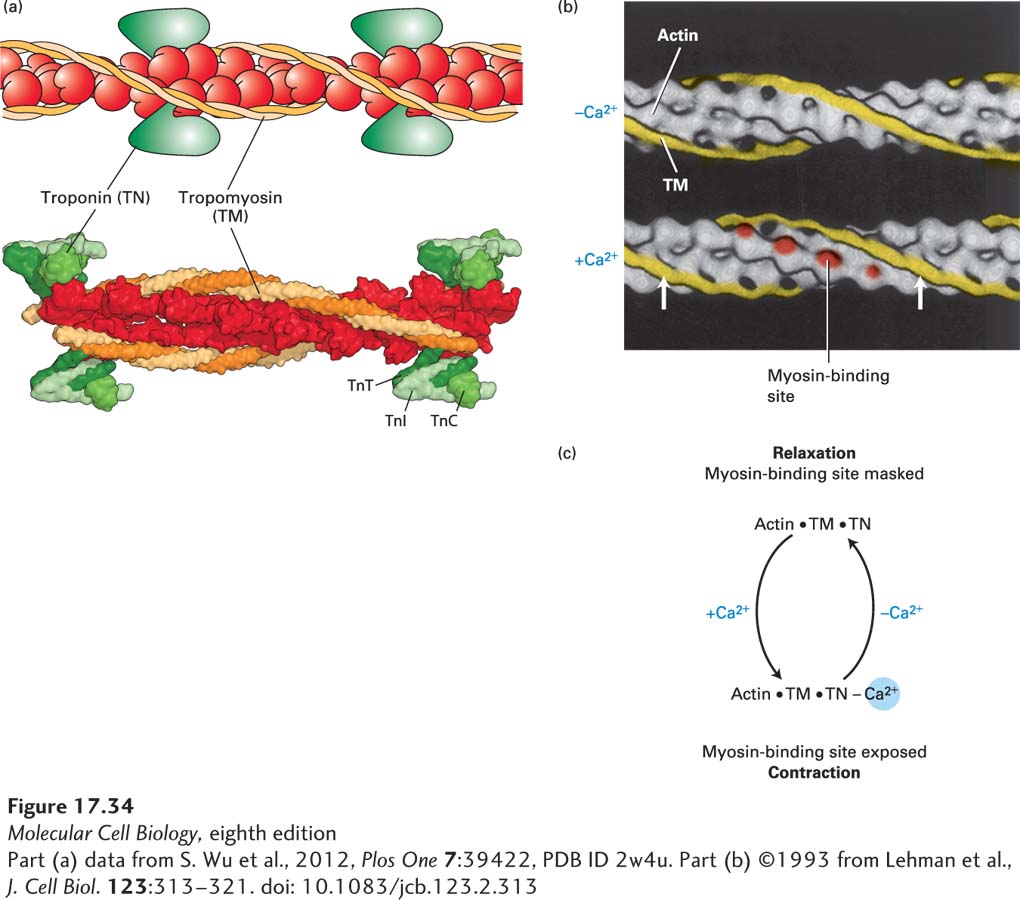
FIGURE 17- 34 Ca2+-dependent thin- filament regulation of skeletal muscle contraction. (a) Model and the corresponding structure of the tropomyosin- troponin regulatory complex on a thin filament. Troponin is a protein complex that is bound to the long α-helical tropomyosin molecule. (b) Three- dimensional electron- microscope reconstructions of the tropomyosin helix (yellow) on a muscle thin filament. Tropomyosin in the relaxed state (top) shifts to a new position (arrows) in the state inducing contraction (bottom) when the Ca2+ concentration in the sarcoplasm increases. This movement exposes myosin- binding sites (red) on actin. (Troponin is not shown in this representation, but it remains bound to tropomyosin in both states.) (c) Summary of the regulation of skeletal muscle contraction by Ca2+ binding to troponin.
[Part (a) data from S. Wu et al., 2012, Plos One 7:39422, PDB ID 2w4u. Part (b) ©1993 from Lehman et al., J. Cell Biol. 123:313– 321. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.2.313]
[Leave] [Close]