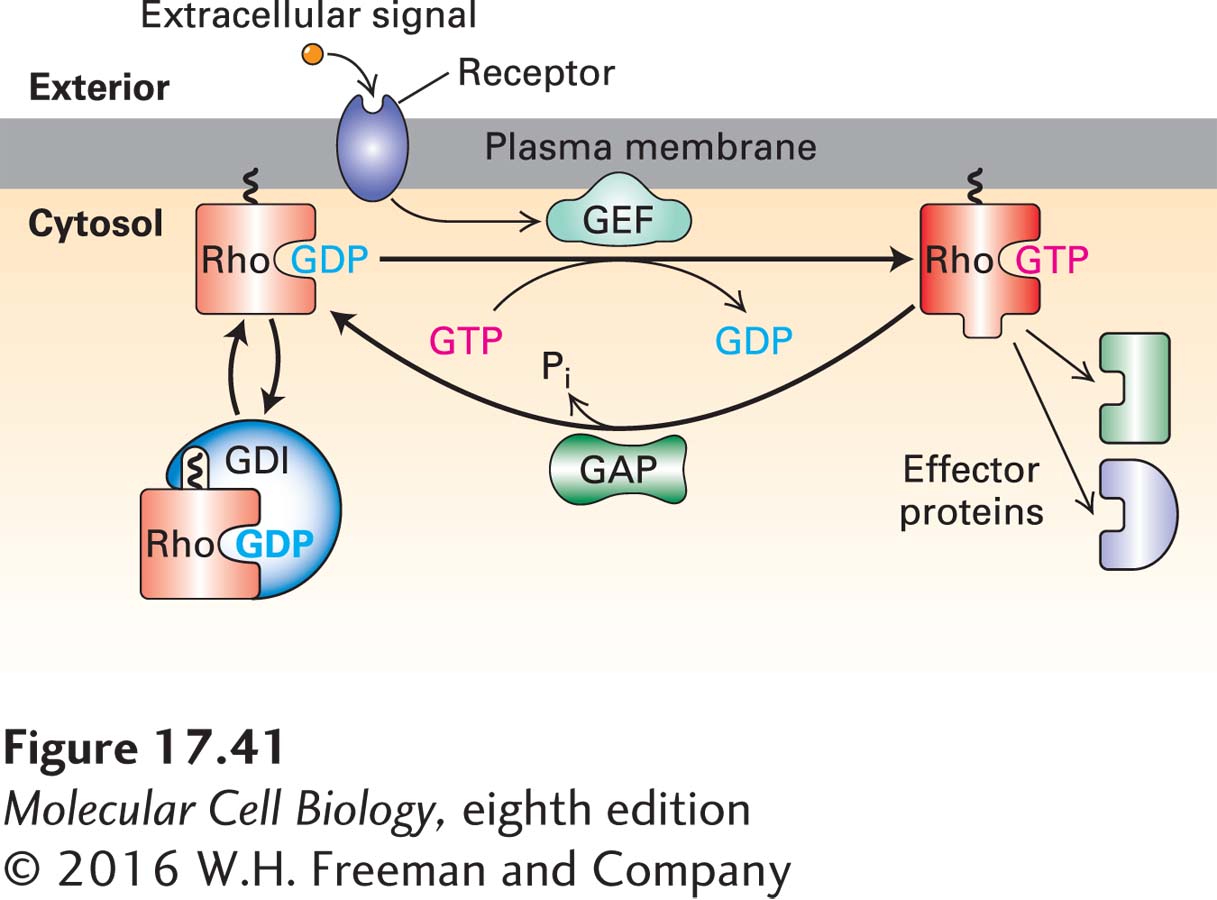
FIGURE 17- 41 Regulation of the Rho family of small GTPases. The small GTPases of the Rho family are molecular switches regulated by accessory proteins. Rho proteins exist in the Rho- GDP bound form complexed with a protein known as GDI (guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor), which keeps them in an inactive state in the cytosol. Membrane- bound signaling pathways bring Rho proteins to the membrane and, through the action of a GEF (guanine nucleotide exchange factor), exchange the GDP for GTP, thus activating them. Membrane- bound activated Rho- GTP can then bind effector proteins that cause changes in the actin cytoskeleton. The Rho protein remains in the active Rho- GTP state until acted on by a GAP (GTPase- activating protein), which allows it to interact with the GDI and be returned to the cytoplasm. See S. Etienne- Manneville and A. Hall, 2002, Nature 420:629.
[Leave] [Close]