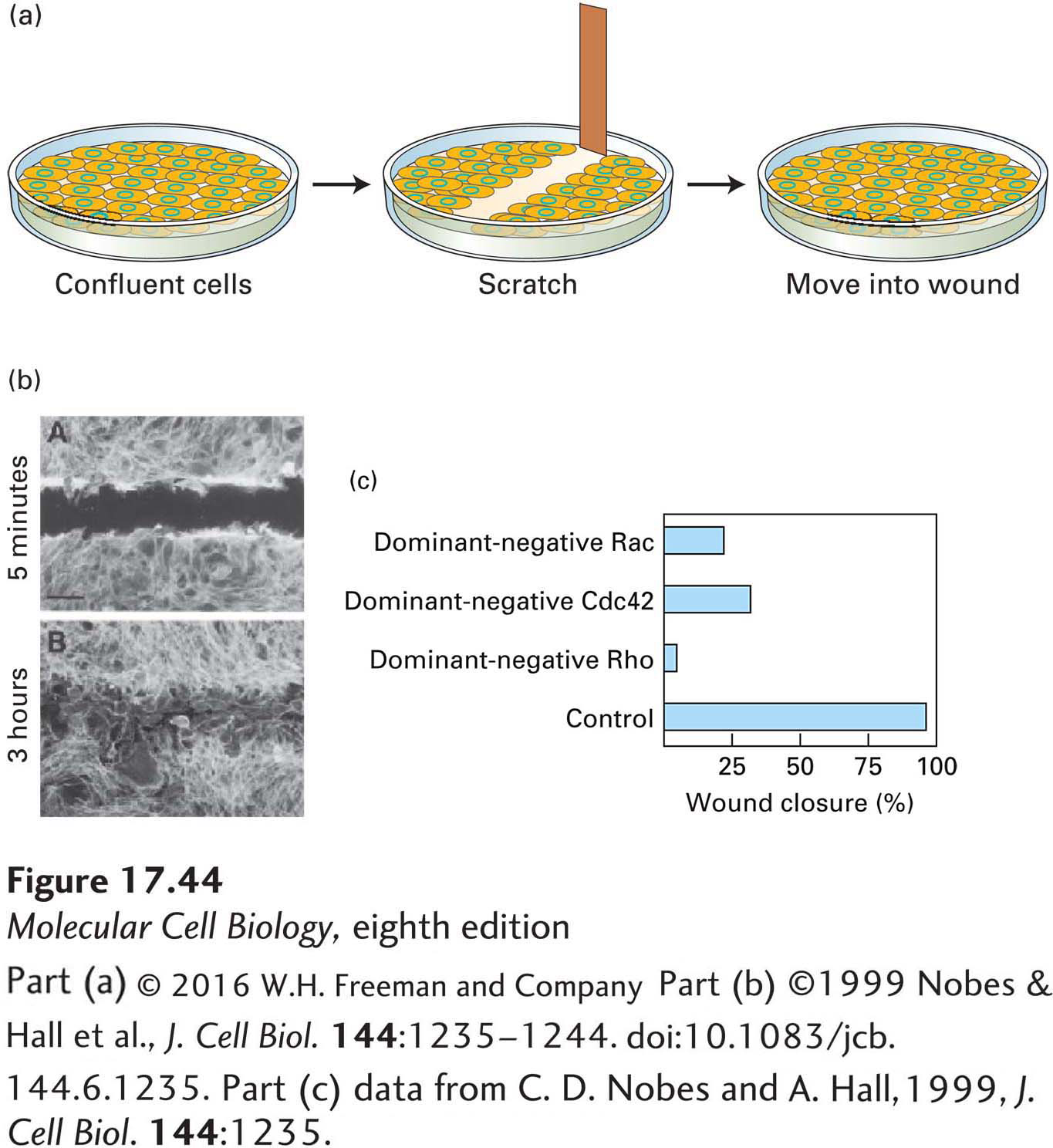
EXPERIMENTAL FIGURE 17- 44 The wounded- cell monolayer assay can be used to dissect signaling pathways in directed cell movement. (a) A confluent layer of cells is scratched to remove a swath about three cells wide to generate a free cell border. The remaining cells detect the free space and newly exposed extracellular matrix and, over a period of hours, fill in the area. (b) Localization of actin in a wounded monolayer 5 minutes and 3 hours after scratching; after 3 hours, cells have migrated into the wounded area. (c) Effect of introducing dominant- negative Cdc42, Rac, and Rho into cells at the wound edge; all affect wound closure.
[Part (b) ©1999 Nobes & Hall et al., J. Cell Biol. 144:1235– 1244. doi:10.1083/jcb.144.6.1235. Part (c) data from C. D. Nobes and A. Hall, 1999, J. Cell Biol. 144:1235.]
[Leave] [Close]