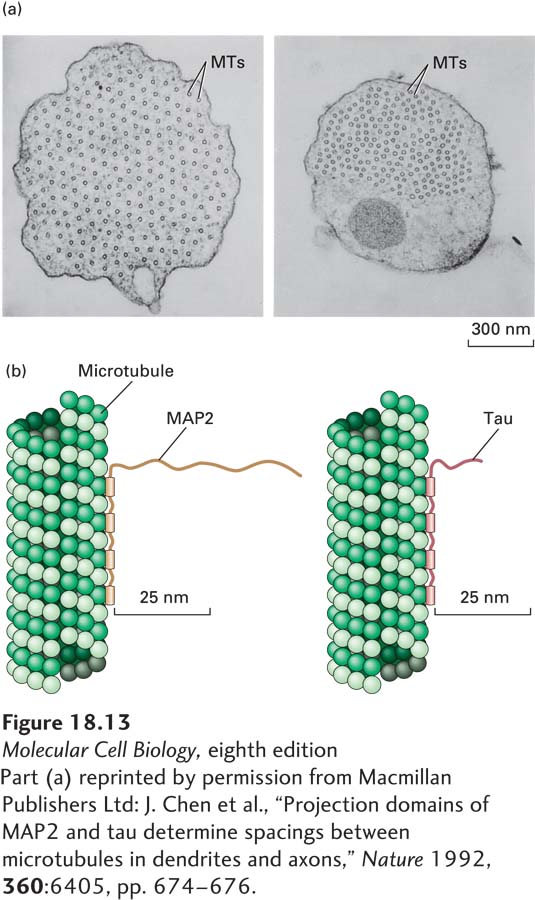
EXPERIMENTAL FIGURE 18- e- n- 2- u- n-
[Part (a) reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: J. Chen et al., “Projection domains of MAP2 and tau determine spacings between microtubules in dendrites and axons,” Nature 1992, 360:6405, pp. 674-