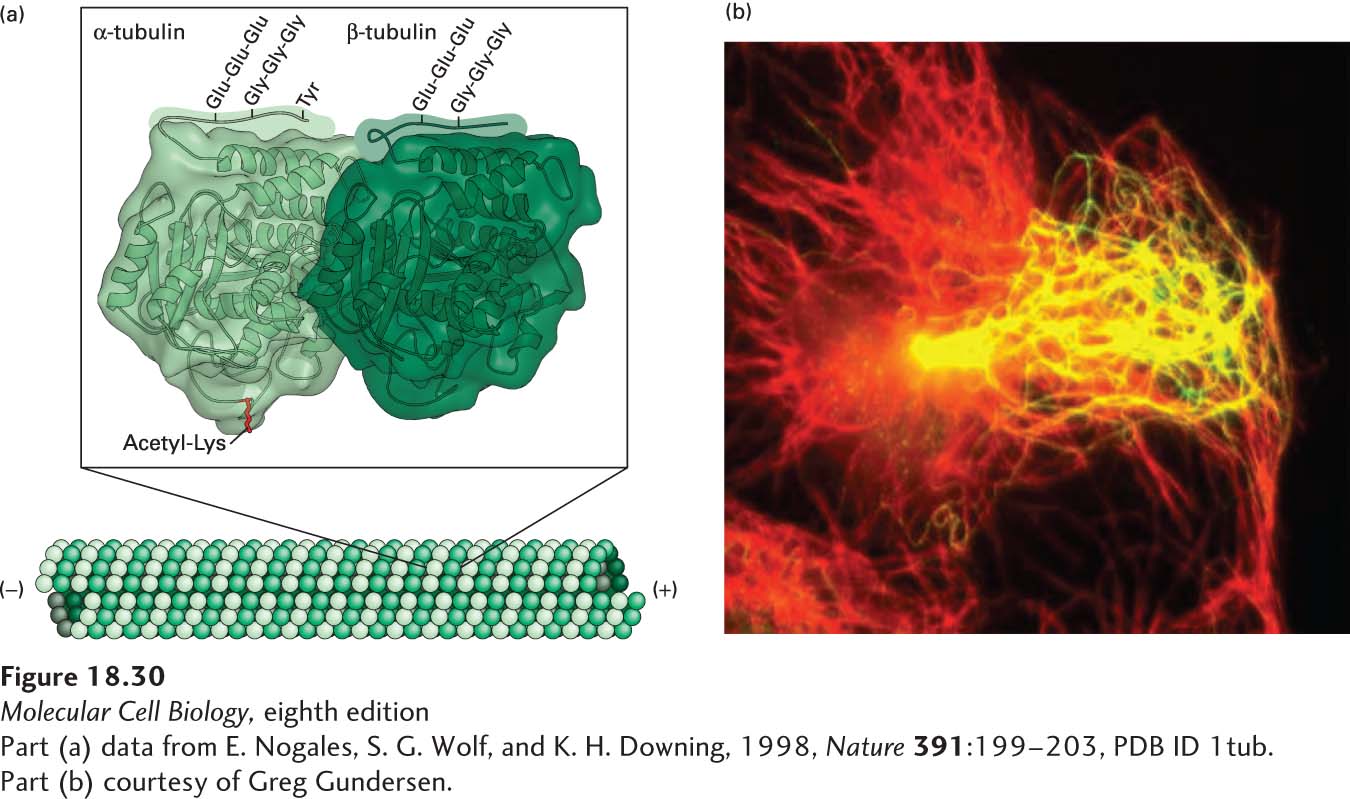
EXPERIMENTAL FIGURE 18- t- 1–
[Part (a) data from E. Nogales, S. G. Wolf, and K. H. Downing, 1998, Nature 391:199–