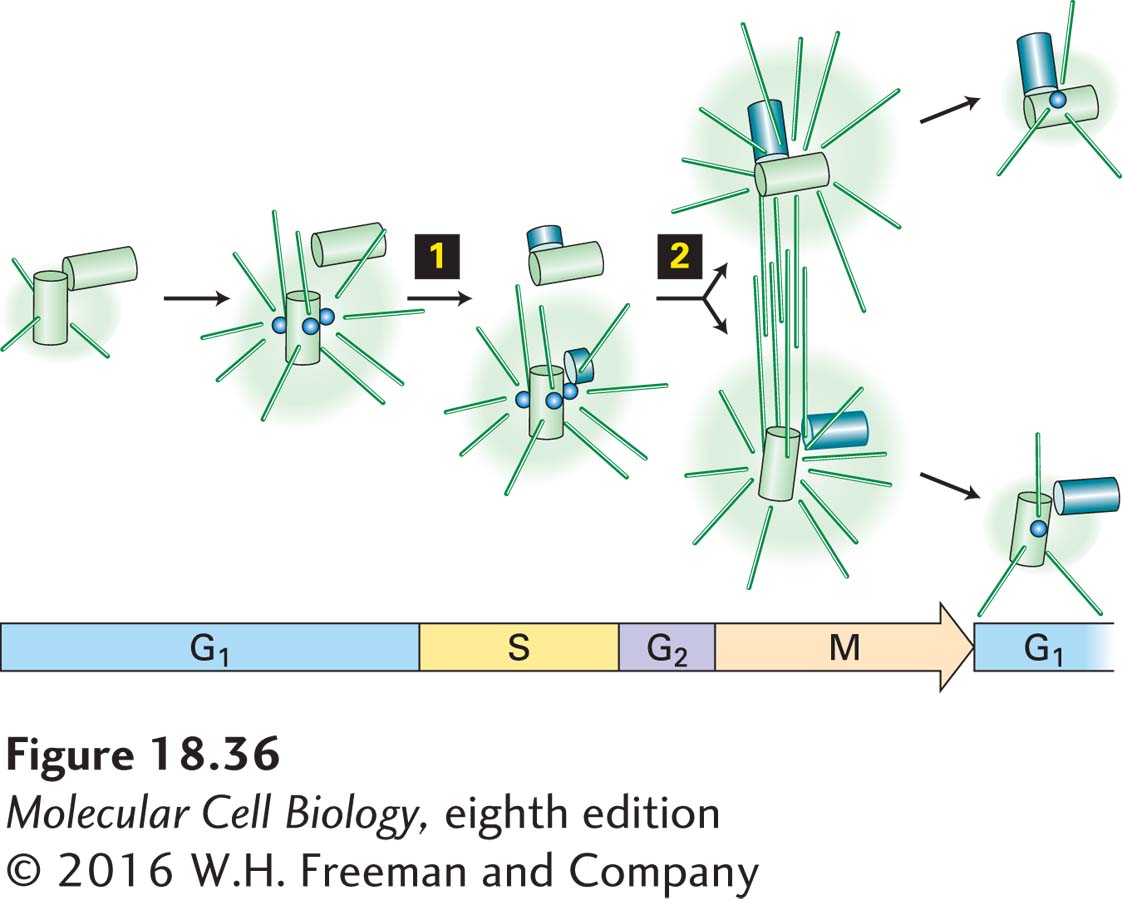
FIGURE 18- 36 Relation of centrosome duplication to the cell cycle. Centrosome duplication, which is initiated by the G1/S phase CDKs and Plk4 (step 1), results in the pair of centrioles (green) separating and a daughter centriole (blue) budding from each. By the G2 phase, growth of the daughter centrioles is complete, but the two pairs of centrioles remain within a single centrosomal complex. Early in mitosis, driven by the activation of M phase CDKs (step 2), the centrosome splits, each half nucleates assembly of microtubules, and the two centriole pairs are moved to opposite sides of the nucleus. The amount of pericentriolar material and the microtubule nucleation activity of the centrosomes increases greatly in mitosis. In mitosis, each MTOC is called a spindle pole.
[Leave] [Close]