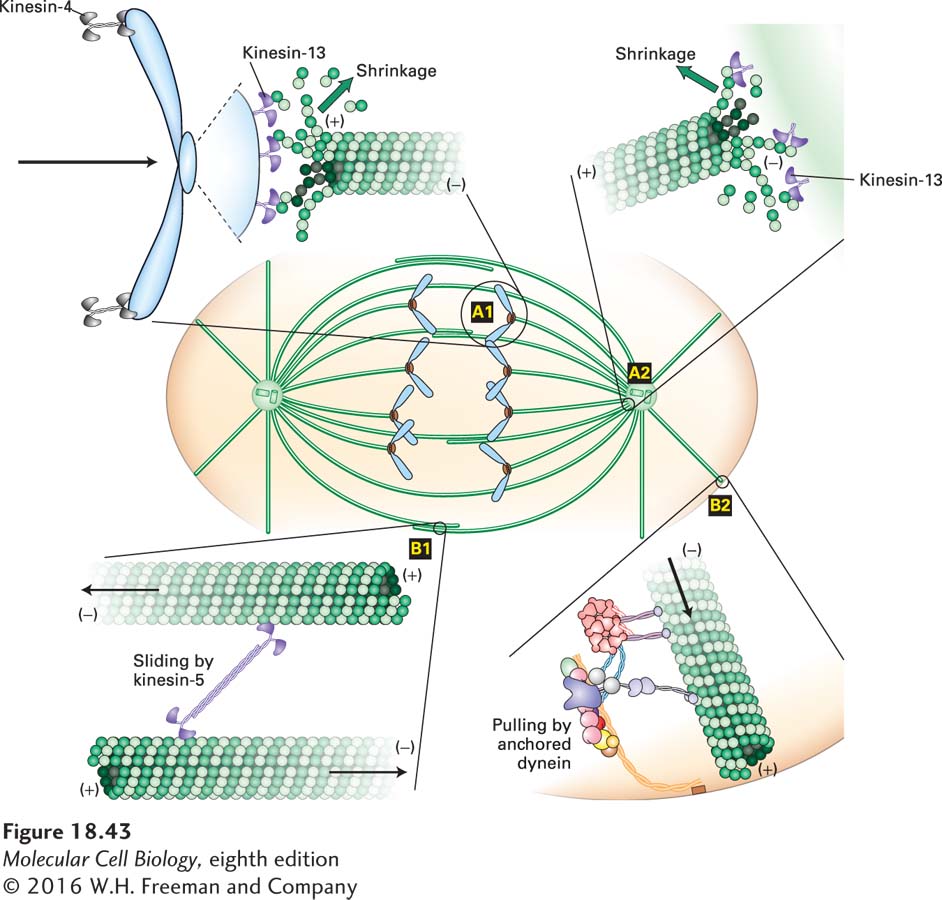
FIGURE 18- e- n- n- n- d– n- 7–