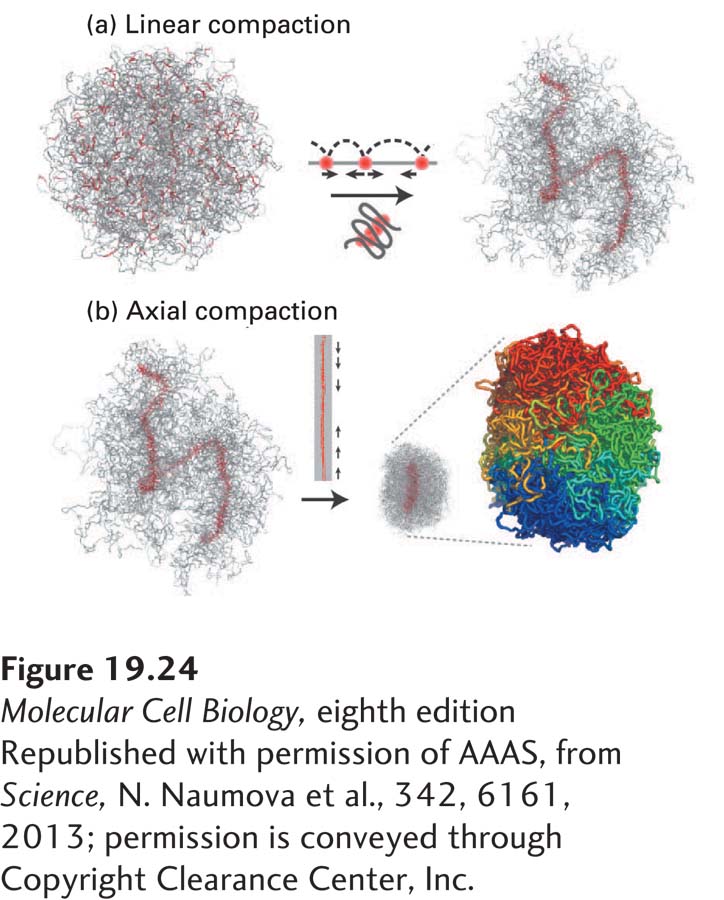
Figure 19-
[Republished with permission of AAAS, from Science, N. Naumova et al., 342, 6161, 2013; permission is conveyed through Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.]