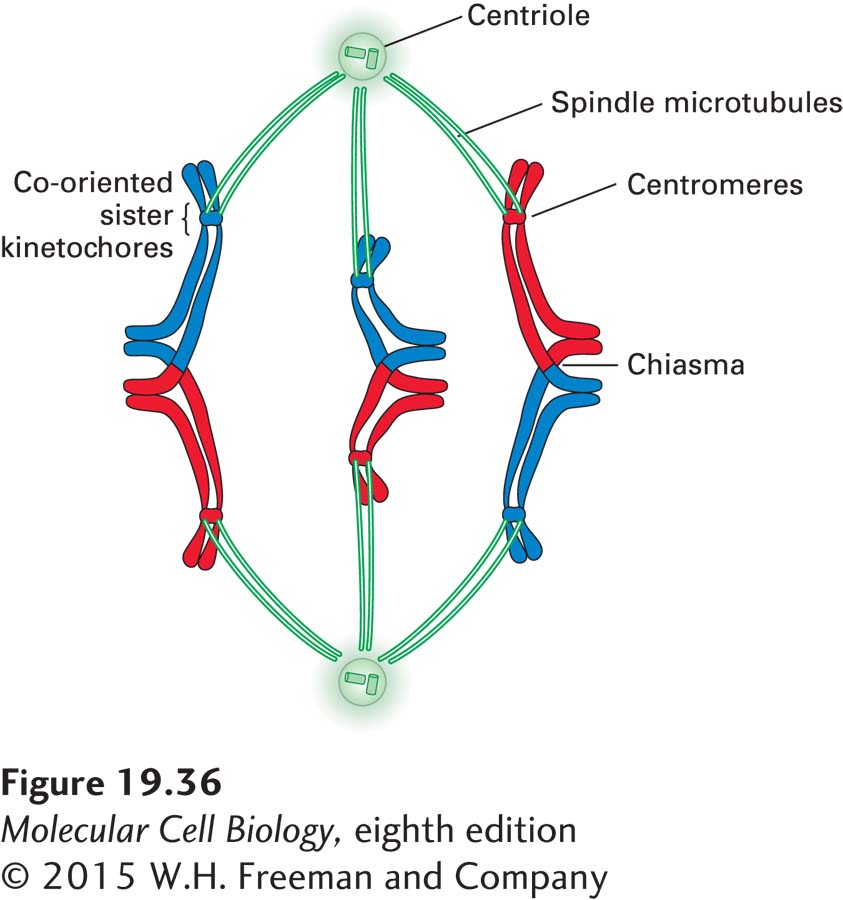
Figure 19-