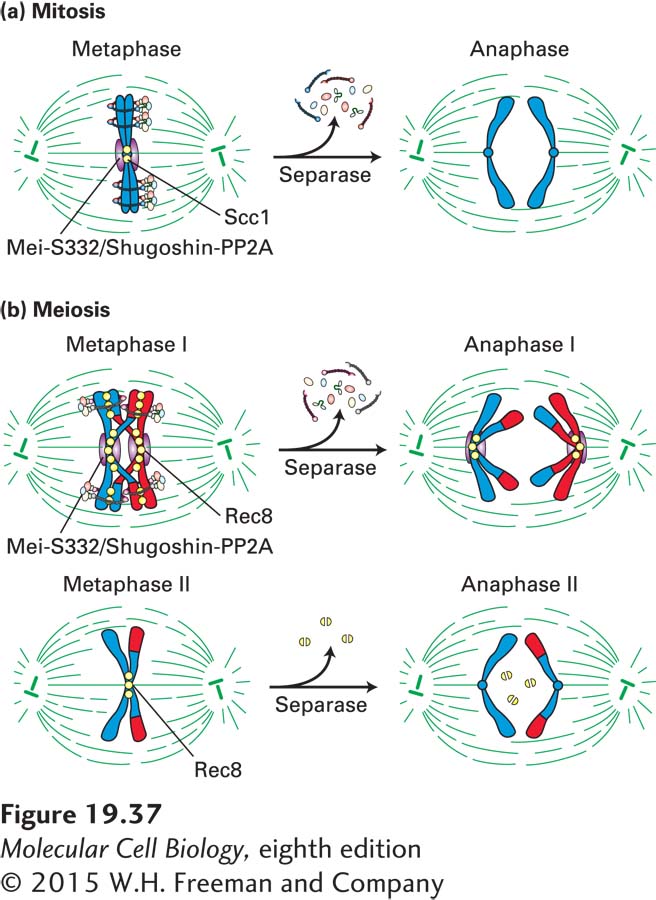
Figure 19- 37 Cohesin function during mitosis and meiosis. (a) During mitosis, sister chromatids generated by DNA replication in S phase are initially linked by cohesin complexes along the length of the chromatids. During chromosome condensation, cohesin complexes (yellow) become restricted to the region of the centromere at metaphase. Mei- S332/Shugoshin (purple) recruits PP2A to centromeres, where they antagonize Polo kinase and Aurora B, preventing the dissociation of cohesins from centromeric regions. Dissociation of Mei- S332/Shugoshin from centromeres and activation of separase leads to removal of cohesins at the centromere. Sister chromatids now separate, marking the onset of anaphase. (b) In prophase of meiosis I, maternal and paternal chromatids establish linkages between each other by homologous recombination. By metaphase I, the chromatids of each replicated chromosome are cross- linked by cohesin complexes along their full length. Rec8, a meiosis- specific homolog of Scc1, is cleaved along chromosome arms but not around the centromere, allowing homologous chromosome pairs to segregate to daughter cells. Centromeric Rec8 is protected from cleavage by PP2A, recruited to centromeric regions by the PP2A regulator Mei- S332/Shugoshin (shown in purple). By metaphase II, the Mei- S332/Shugoshin- PP2A complex dissociates from chromosomes. Cohesins can now be cleaved during meiosis II, allowing sister chromatids to segregate. See F. Uhlmann, 2001, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13:754.
[Leave] [Close]