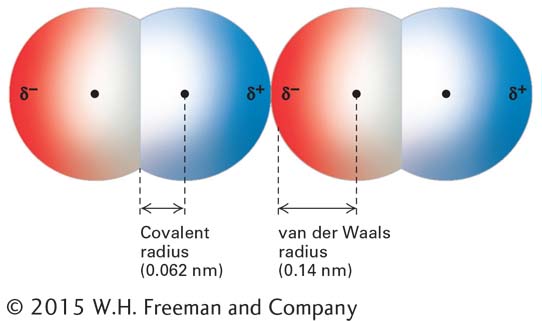
FIGURE 2- 10 Two oxygen molecules in van der Waals contact. In this model, red indicates negative charge and blue indicates positive charge. Transient dipoles in the electron clouds of all atoms give rise to weak attractive forces, called van der Waals interactions. Each type of atom has a characteristic van der Waals radius at which van der Waals interactions with other atoms are optimal. Because atoms repel one another if they are close enough together for their outer electrons to overlap without being shared in a covalent bond, the van der Waals radius is a measure of the size of the electron cloud surrounding an atom. The covalent radius indicated here is for the double bond of O=O; the single- bond covalent radius of oxygen is slightly longer.
[Leave] [Close]