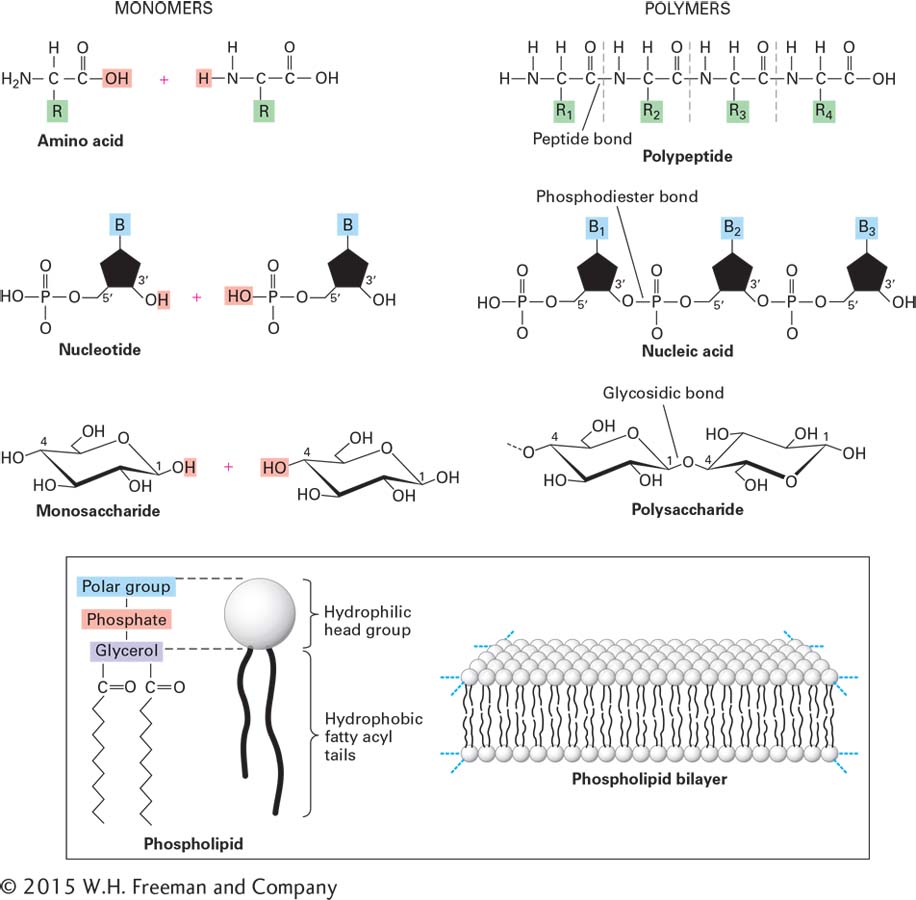
FIGURE 2- 13 Overview of the cell’s principal chemical building blocks. (Top) The three major types of biological macromolecules are each assembled by the polymerization of multiple small molecules (monomers) of a particular type: proteins from amino acids (see Chapter 3), nucleic acids from nucleotides (see Chapter 5), and polysaccharides from monosaccharides (sugars). Each monomer is covalently linked into the polymer by a reaction whose net result is loss of a water molecule (dehydration). (Bottom) In contrast, phospholipid monomers noncovalently assemble into a bilayer structure, which forms the basis of all cellular membranes (see Chapter 7).
[Leave] [Close]