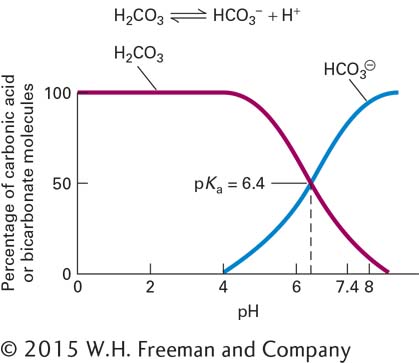
FIGURE 2- 26 The relationship between pH, pKa, and the dissociation of an acid. As the pH of a solution of carbonic acid rises from 0 to 8.5, the percentage of the compound in the undissociated, or un- ionized, form (H2CO3) decreases from 100 percent and that of the ionized form increases from 0 percent. When the pH (6.4) is equal to the acid’s pKa, half of the carbonic acid has ionized. When the pH rises to above 8, virtually all of the acid has ionized to the bicarbonate form (HCO3–).
[Leave] [Close]