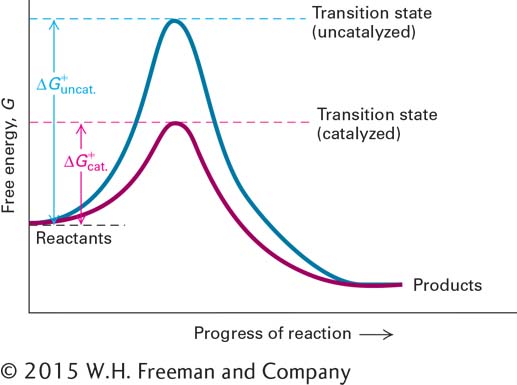
FIGURE 2- h-