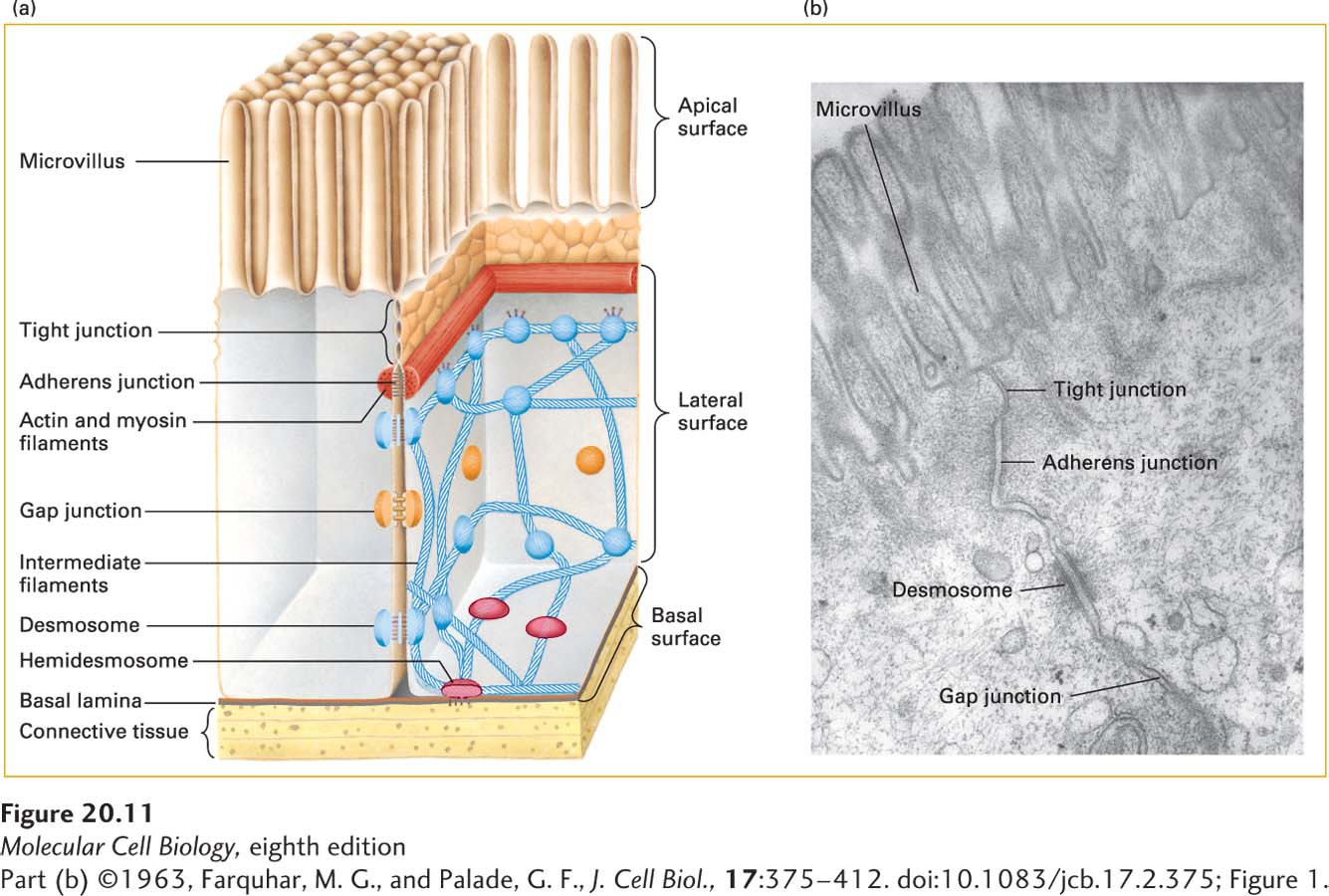
FIGURE 20- 11 Principal types of cell junctions connecting the columnar epithelial cells lining the small intestine. (a) Schematic cutaway drawing of intestinal epithelial cells. The basal surface of the cells rests on a basal lamina, and the apical surface is packed with fingerlike microvilli that project into the intestinal lumen. Tight junctions, lying just under the microvilli, prevent the diffusion of many substances between the intestinal lumen and internal body fluids (such as the blood) via the extracellular space between cells. Gap junctions allow the movement of small molecules and ions between the cytosols of adjacent cells. The remaining three types of junctions— adherens junctions, desmosomes, and hemidesmosomes— are critical to cell- cell and cell- matrix adhesion and signaling. (b) Electron micrograph of a thin section of epithelial cells in the rat intestine, showing the relative locations of the different junctions.
[Part (b) ©1963, Farquhar, M. G., and Palade, G. F., J. Cell Biol., 17:375– 412. doi:10.1083/jcb.17.2.375; Figure 1.]
[Leave] [Close]