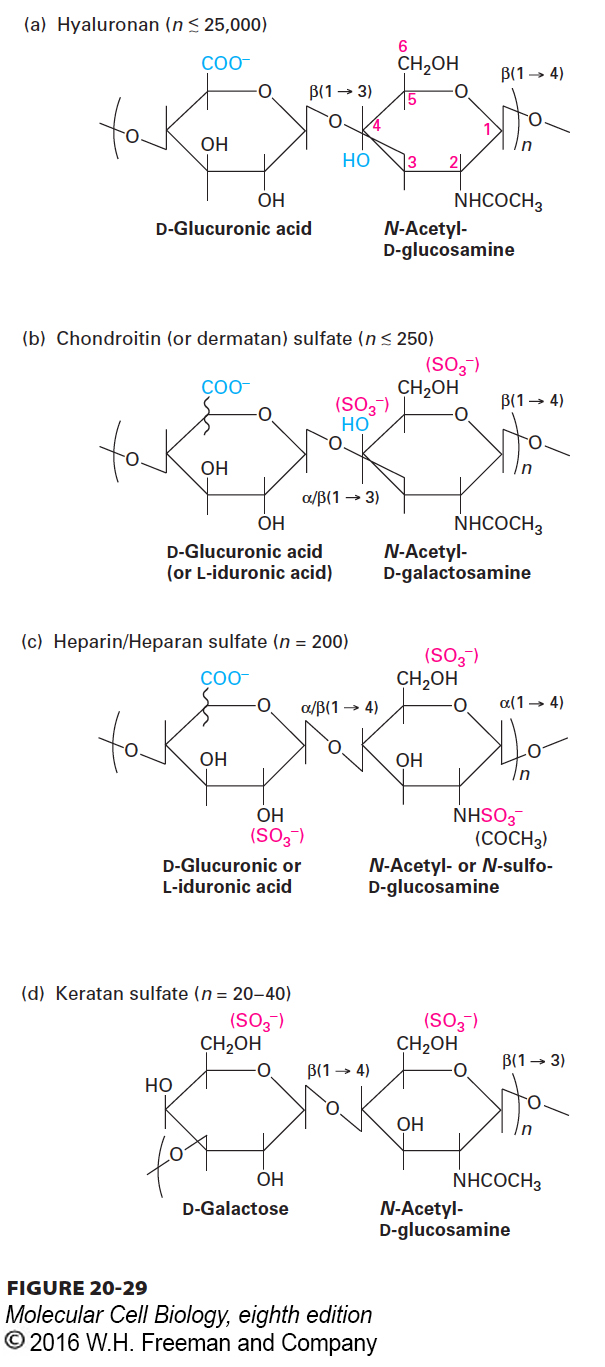
FIGURE 20- 29 The repeating disaccharides of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). Each of the four classes of GAGs is formed by polymerization of monomeric units into repeats of a particular disaccharide and subsequent modifications, including addition of sulfate groups and inversion (epimerization) of the carboxyl group on carbon 5 of D-glucuronic acid to yield L-iduronic acid. The squiggly lines represent covalent bonds that are oriented either above (D-glucuronic acid) or below (L-iduronic acid) the ring. Heparin is generated by hypersulfation of heparan sulfate, whereas hyaluronan is nonsulfated.
[Leave] [Close]