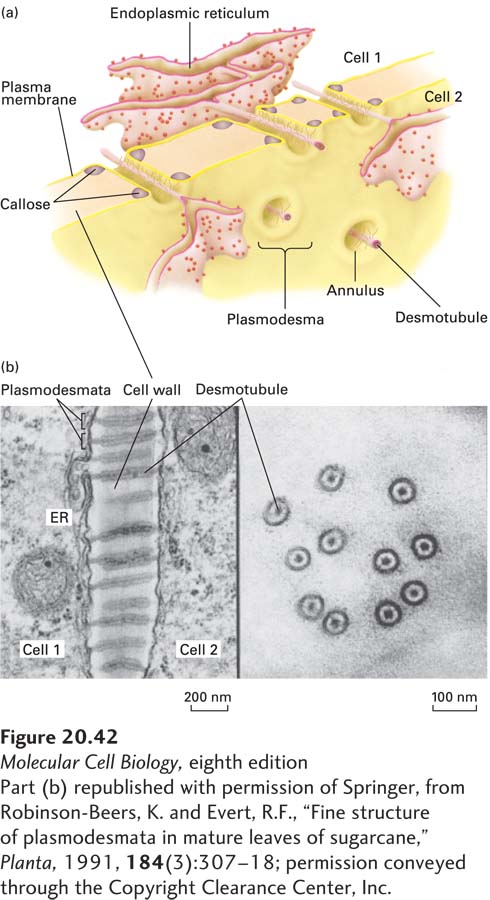
FIGURE 20- 42 Plasmodesmata. (a) Schematic model of plasmodesmata, showing the desmotubule, an extension of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and the annulus, a plasma- membrane- lined channel filled with cytosol that interconnects the cytosols of adjacent cells. The regulated deposition of a glucose polymer called callose (cyan) in the extracellular spaces in the cell wall adjacent to the entrances of the channels has the potential to block intercellular transport through the plasmodesmata, apparently by forcing the closing of the channels by narrowing the annulus. (b) Electron micrographs of thin sections of a sugarcane leaf (brackets indicate individual plasmodesmata). Left: Longitudinal view, showing ER and desmotubule running through each annulus. Right: Perpendicular cross- sectional views of plasmodesmata, in some of which spoke structures connecting the plasma membrane to the desmotubule can be seen.
[Part (b) republished with permission of Springer, from Robinson- Beers, K. and Evert, R.F., “Fine structure of plasmodesmata in mature leaves of sugarcane,” Planta, 1991, 184(3):307– 18; permission conveyed through the Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.]
[Leave] [Close]