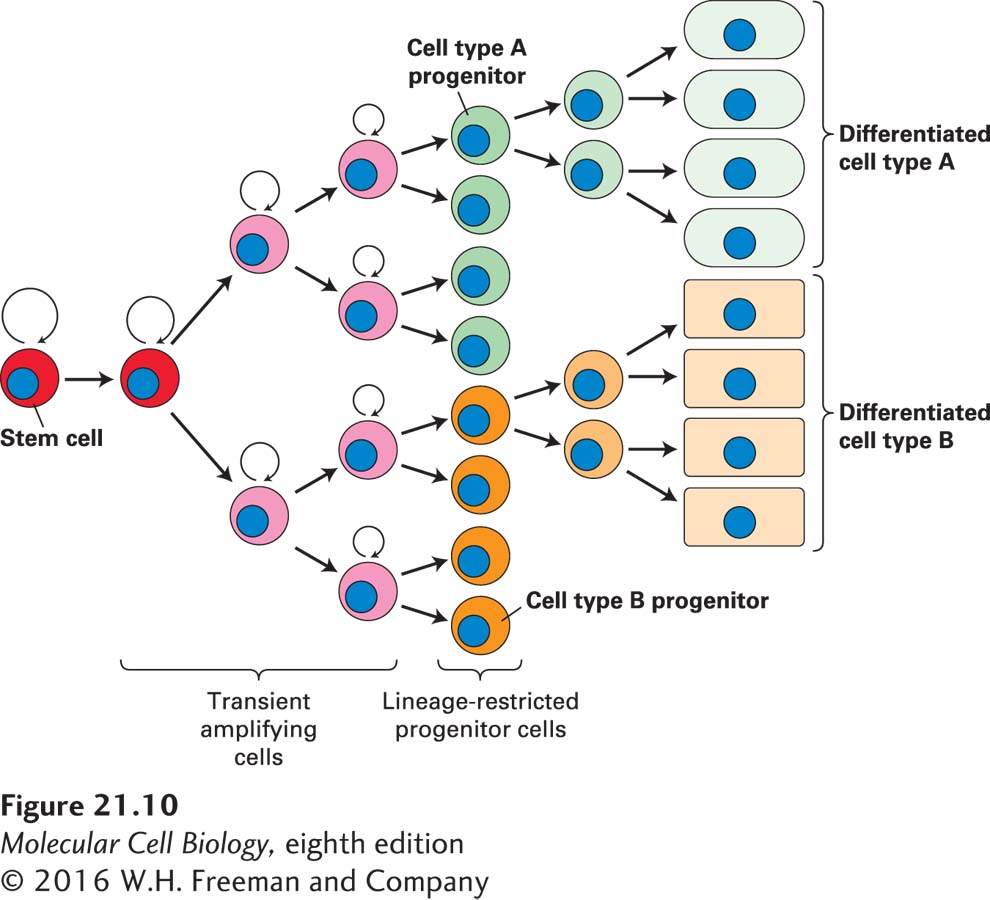
FIGURE 21- 10 The pathway from stem cells to lineage- restricted progenitors to differentiated cells. On average, during each division of a multipotent somatic stem cell, at least one of the daughter cells becomes a stem cell like the parent cell. Stem cells thus undergo self- renewal divisions such that the number of stem cells of a particular type stays constant or increases during the organism’s lifetime. Other daughter cells, termed transient amplifying cells, divide rapidly and undergo limited numbers of self- renewal divisions, but ultimately produce lineage- restricted progenitor cells. These cells cannot undergo self- renewal divisions, but can divide and produce differentiated cells of a particular type.
[Leave] [Close]