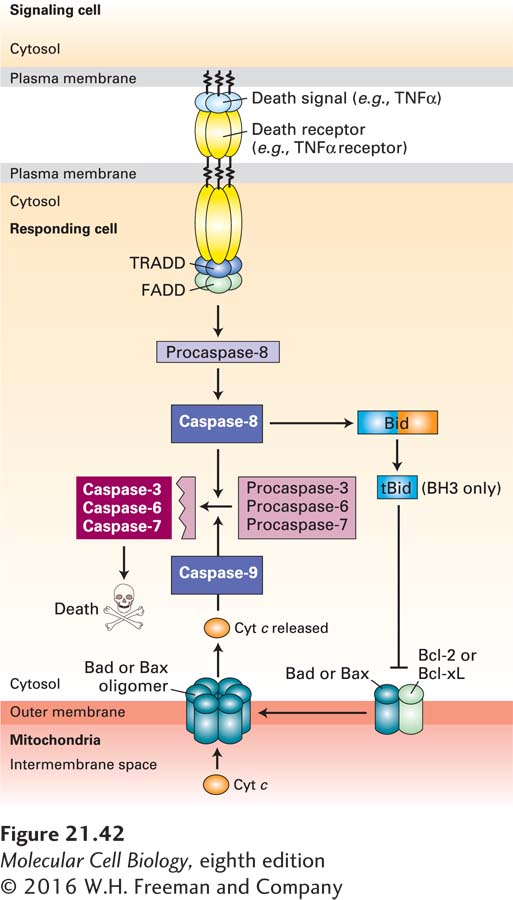
FIGURE 21- 42 Cell murder: the extrinsic apoptosis pathway. Extrinsic (or death receptor– regulated) apoptosis pathways are found in many types of cells. In this example, binding of TNFα on the surface of one cell to the TNFα death receptor on an adjacent cell leads to recruitment of the adapter proteins TRADD (TNF receptor- associated death domain protein) and FADD (Fas- associated death domain protein) and the dimerization and activation of the initiator caspase- 8. Active caspase- 8 then cleaves and activates effector caspases- 3, -6, and -7, which cleave vital cellular proteins and induce cell death. Cleavage of the BH3- only protein Bid (BH3- interacting- domain death agonist) by caspase- 8 generates a tBid fragment that binds to Bcl- 2 on the outer mitochondrial membrane, leading to release of cytochrome c into the cytosol and activation of the intrinsic apoptosis pathway (see Figure 21- 39 ) as well. See P. Bouillet and L. O’Reilly, 2009, Nat. Rev. Immunol. 9:514, and A. Ashkenazi and G. Salvesen, 2014, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 30:20.
[Leave] [Close]