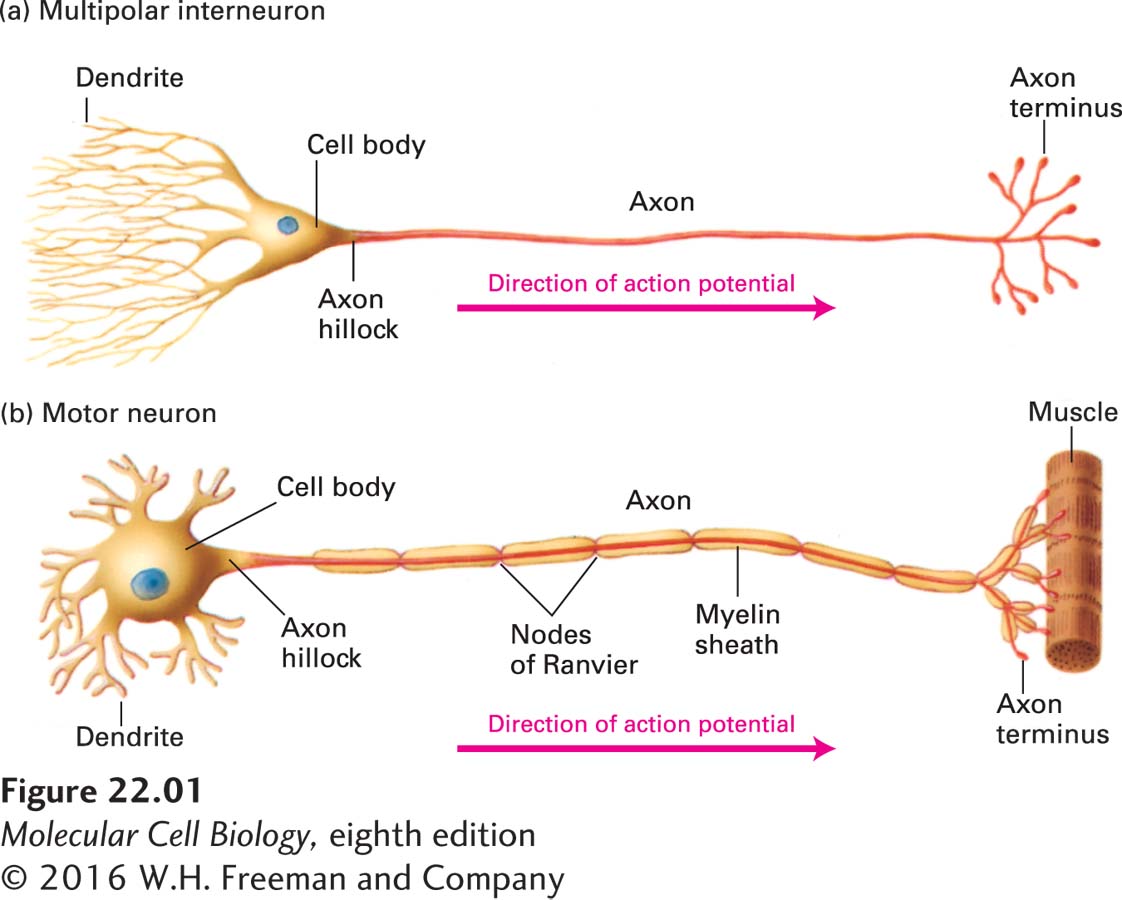
FIGURE 22- 1 Typical morphology of two types of mammalian neurons. Action potentials arise in the axon hillock and are conducted toward the axon terminus. (a) A multipolar interneuron has profusely branched dendrites, which receive signals at synapses with several hundred other neurons. Small voltage changes imparted by inputs in the dendrites can sum to give rise to the more massive action potential, which starts in the hillock. A single long axon that branches laterally at its terminus transmits signals to other neurons. (b) A motor neuron innervating a muscle cell typically has a single long axon extending from the cell body to the effector cell. In mammalian motor neurons, an insulating sheath of myelin usually covers all parts of the axon except at the nodes of Ranvier and the axon termini. The myelin sheath is composed of cells called glia.
[Leave] [Close]