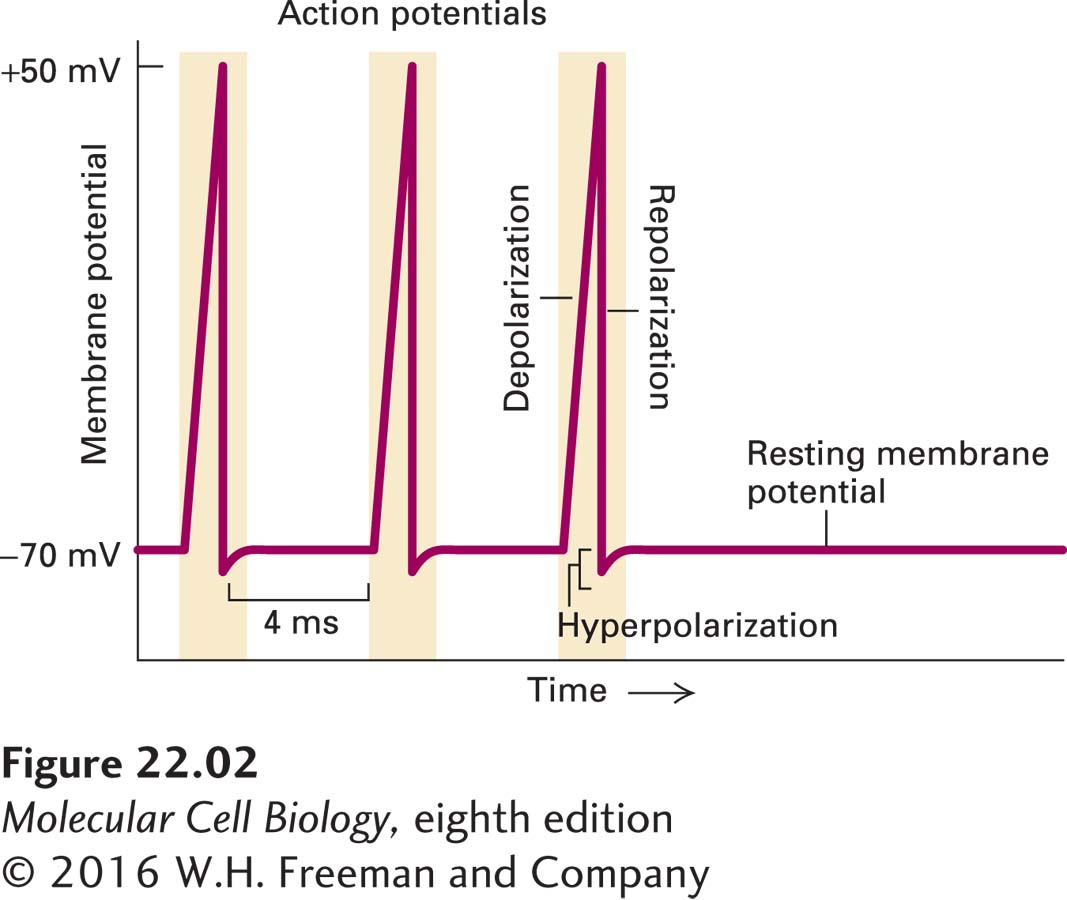
EXPERIMENTAL FIGURE 22- 2 Recording of an axonal membrane potential over time reveals the amplitude and frequency of action potentials. An action potential is a sudden, transient depolarization of the membrane, followed by repolarization to the resting potential of about –70 mV. The axonal membrane potential can be measured with a small electrode placed into it (see Figure 11- 19 ). This recording shows the neuron generating one action potential about every 4 milliseconds.
[Leave] [Close]