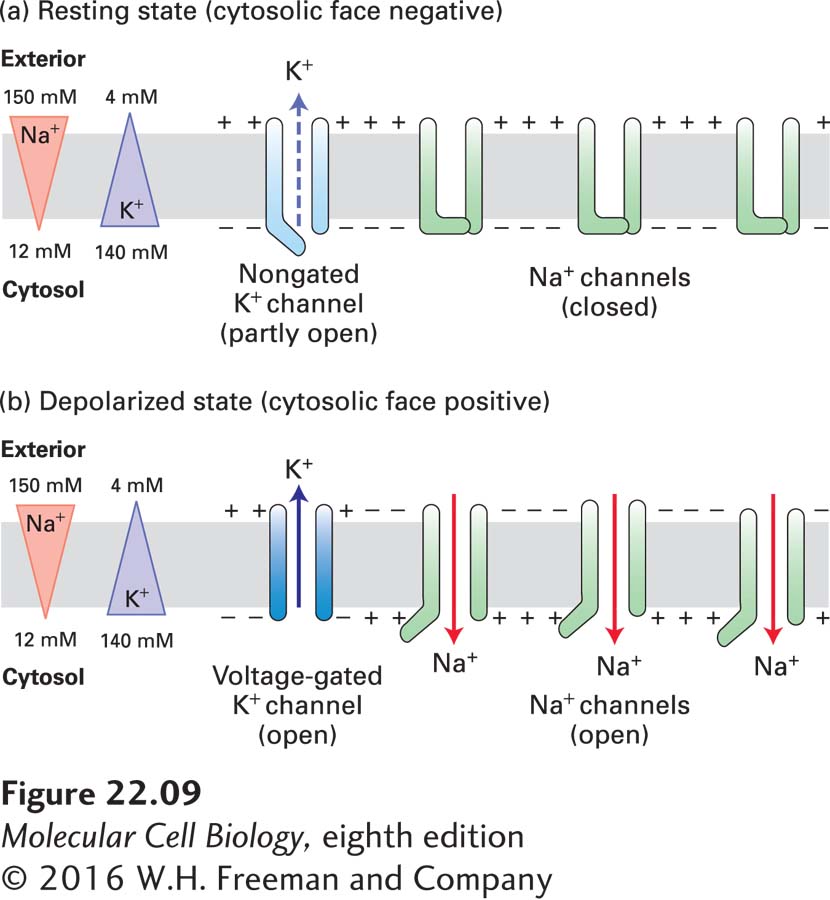
FIGURE 22- 9 Depolarization of the plasma membrane due to opening of gated Na+ channels. (a) In resting neurons, a type of nongated K+ channel is open part of the time, but the more numerous gated Na+ channels are closed. The movement of K+ ions outward establishes the inside- negative membrane potential characteristic of most cells. (b) Opening of gated Na+ channels permits an influx of sufficient Na+ ions to cause a reversal of the membrane potential. In the depolarized state, voltage- gated K+ channels open and subsequently repolarize the membrane. Note that the flows of ions are too small to have much effect on the overall concentration of either Na+ or K+ in the cytosol or exterior fluid.
[Leave] [Close]