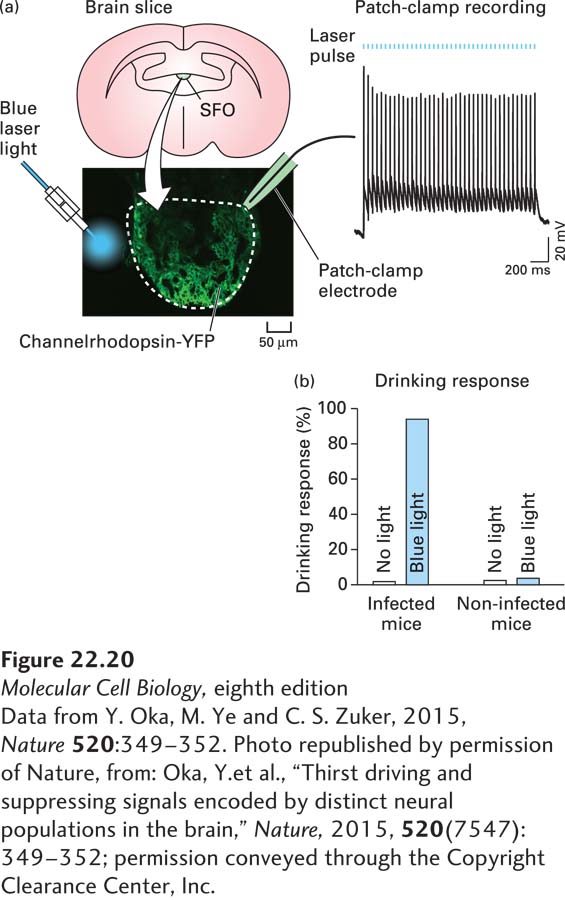
FIGURE 22- 20 Using optogenetics to dissect neural circuits mediating thirst. (a) Channelrhodopsin tagged with a fluorescent protein (YFP) was expressed in excitatory neurons in the subfornical organ (SFO) of the hypothalamus using an excitatory neuron– specific promoter. Neurons expressing channelrhodopsin- YFP were confirmed to be excitable by illumination with blue light in acute hypothalamic slices. (b) When excitatory neurons in the SFO of living mice are activated by blue light, the mice seek water and drink large volumes even if they are well hydrated.
[Data from Y. Oka, M. Ye and C. S. Zuker, 2015, Nature 520:349– 352. Photo republished by permission of Nature, from: Oka, Y. et al., “Thirst driving and suppressing signals encoded by distinct neural populations in the brain,” Nature, 2015, 520(7547):349– 352; permission conveyed through the Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.]
[Leave] [Close]