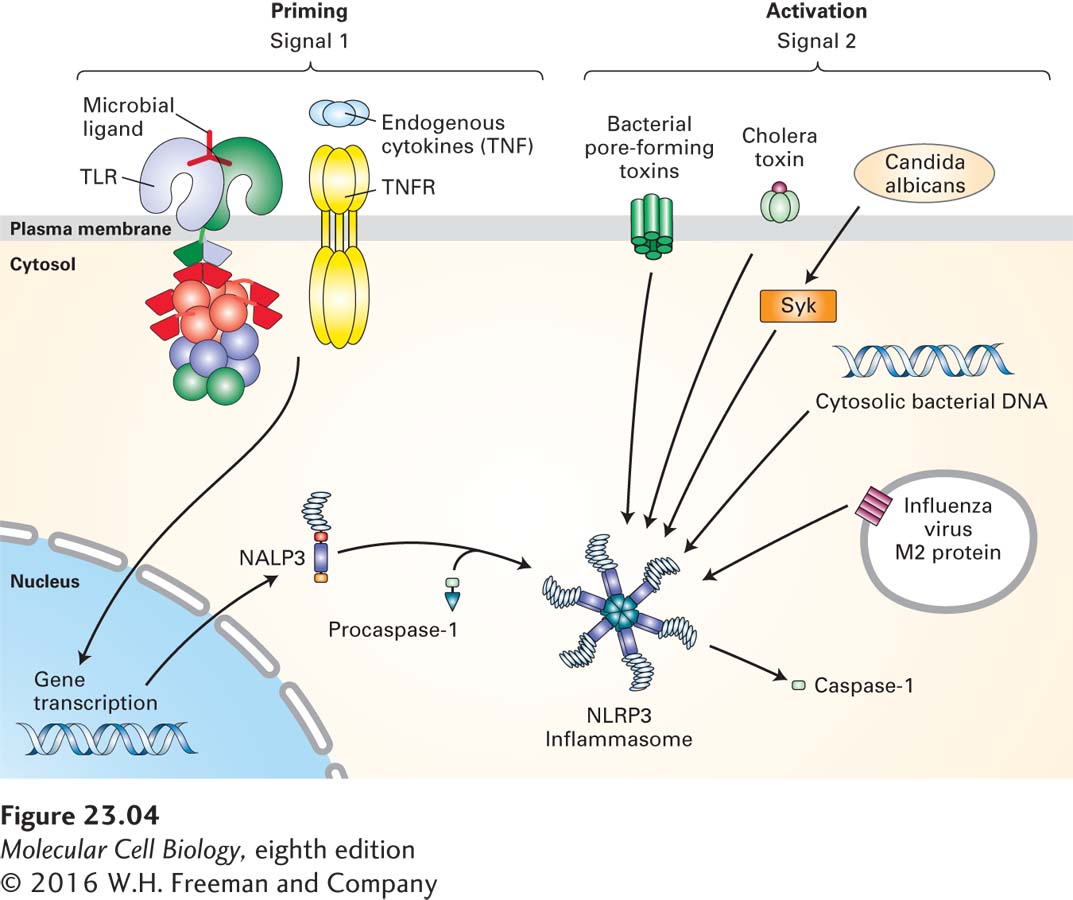
FIGURE 23- e- l- p- o- L- e-