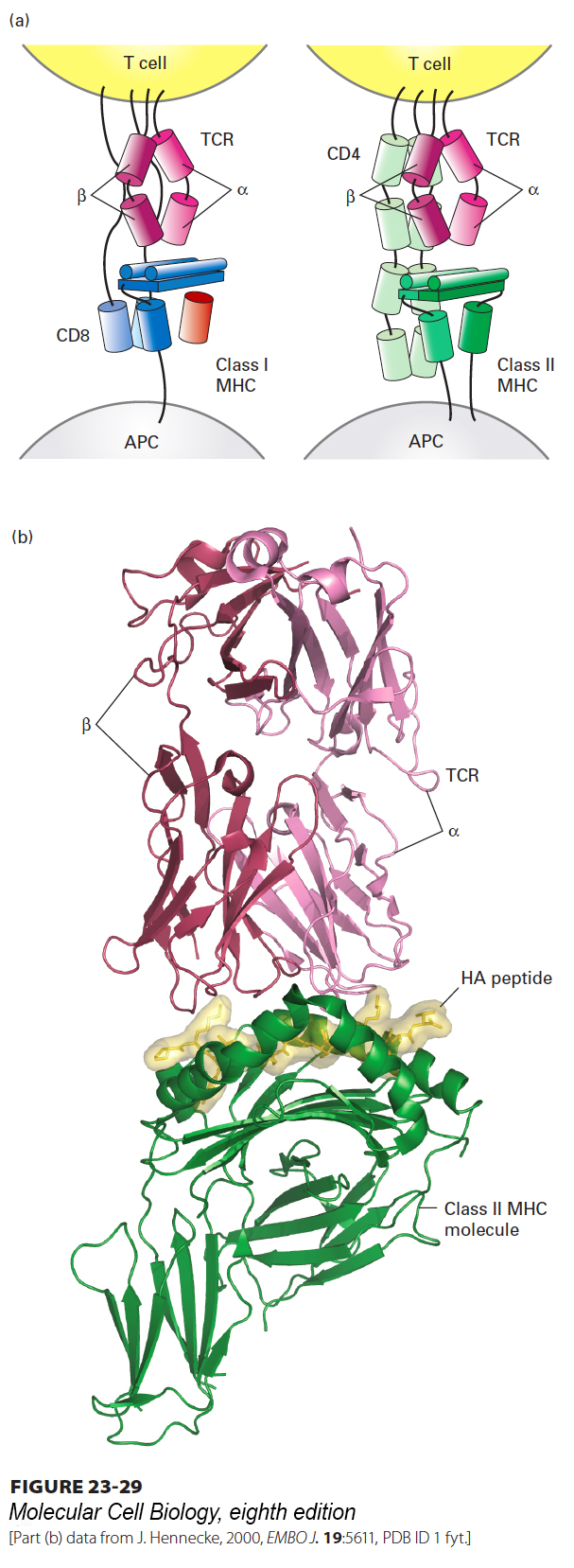
FIGURE 23- T- o- n- T- V- V- D- 3- T- o- n- T- C– x-
[Part (b) data from J. Hennecke, 2000, EMBO J. 19:5611, PDB ID 1 fyt.]