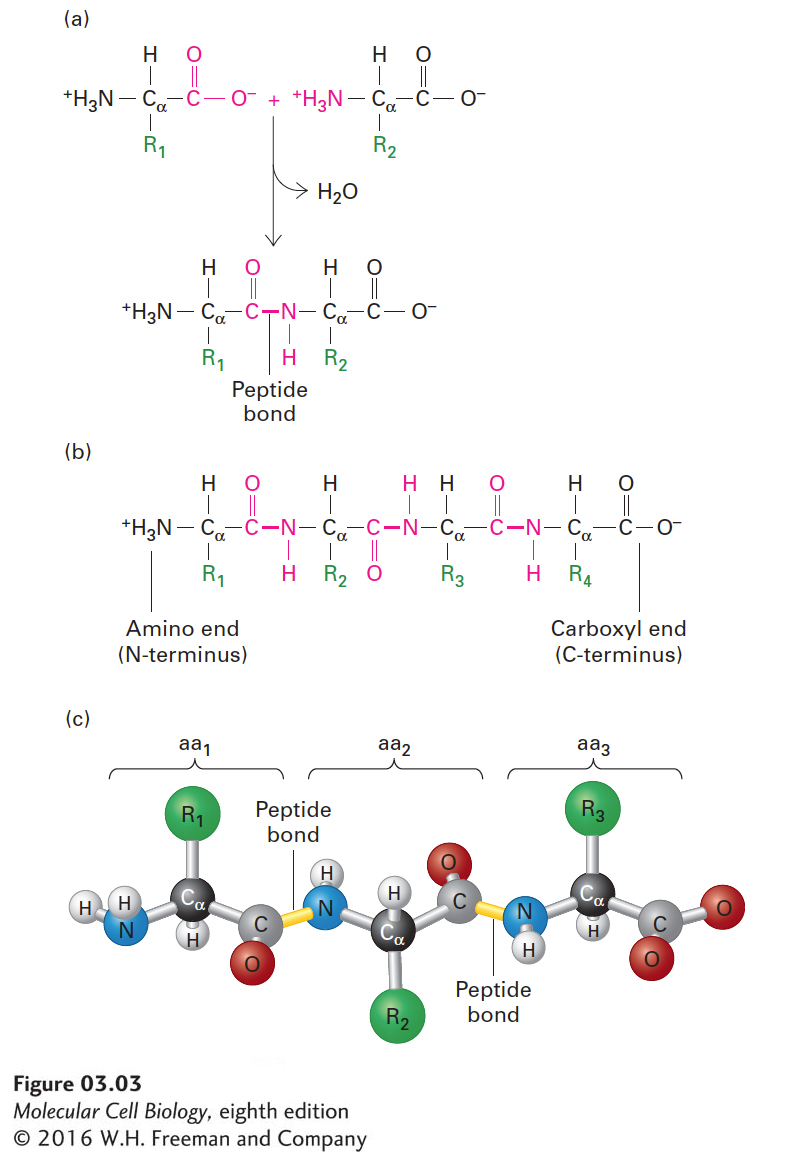
FIGURE 3- 3 Structure of a polypeptide. (a) Individual amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds, which form via reactions that result in a loss of water (dehydration). R1, R2, etc., represent the side chains (“R groups”) of amino acids. (b) Linear polymers of peptide- bond- linked amino acids are called polypeptides, which have a free amino end (N- terminus) and a free carboxyl end (C- terminus). (c) A ball- and- stick model shows peptide bonds (yellow) linking the amino nitrogen atom (blue) of one amino acid (aa) with the carbonyl carbon atom (gray) of an adjacent one in the chain. The R groups (green) extend from the α carbon atoms (black) of the amino acids. These side chains largely determine the distinct properties of individual proteins.
[Leave] [Close]