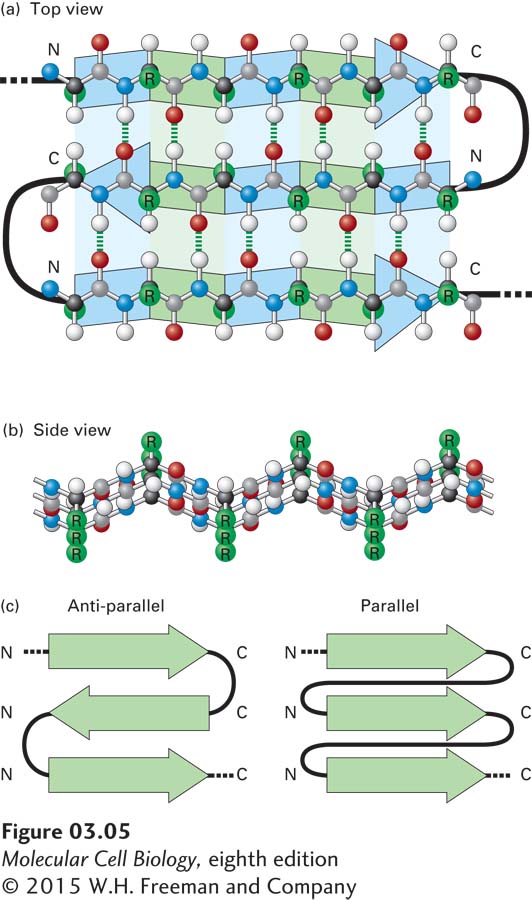
FIGURE 3- 5 The β sheet, another common secondary structure in proteins. (a) Top view of a three- stranded β sheet. Each strand is highlighted by a ribbon- like arrow with alternating blue and green segments that is pointed with an N- to- C orientation, with the loops of connecting residues indicated by thick black lines. In this antiparallel β sheet, each strand (arrow) points in the direction opposite to that of the adjacent strand. The stabilizing hydrogen bonds between the β strands are indicated by green dashed lines. (b) Side view of an antiparallel β sheet. The projection of the R groups (green) above and below the plane of the sheet is obvious in this view. The fixed bond angles in the polypeptide backbone produce a pleated contour represented in panel (a) by the alternating colored segments. (c) Top view of two β sheets, whose individual strands (N- to- C orientations represented by arrows) are either antiparallel, in which the strands alternately point in opposite directions (left), or parallel, in which all strands point in the same direction (right).
[Leave] [Close]