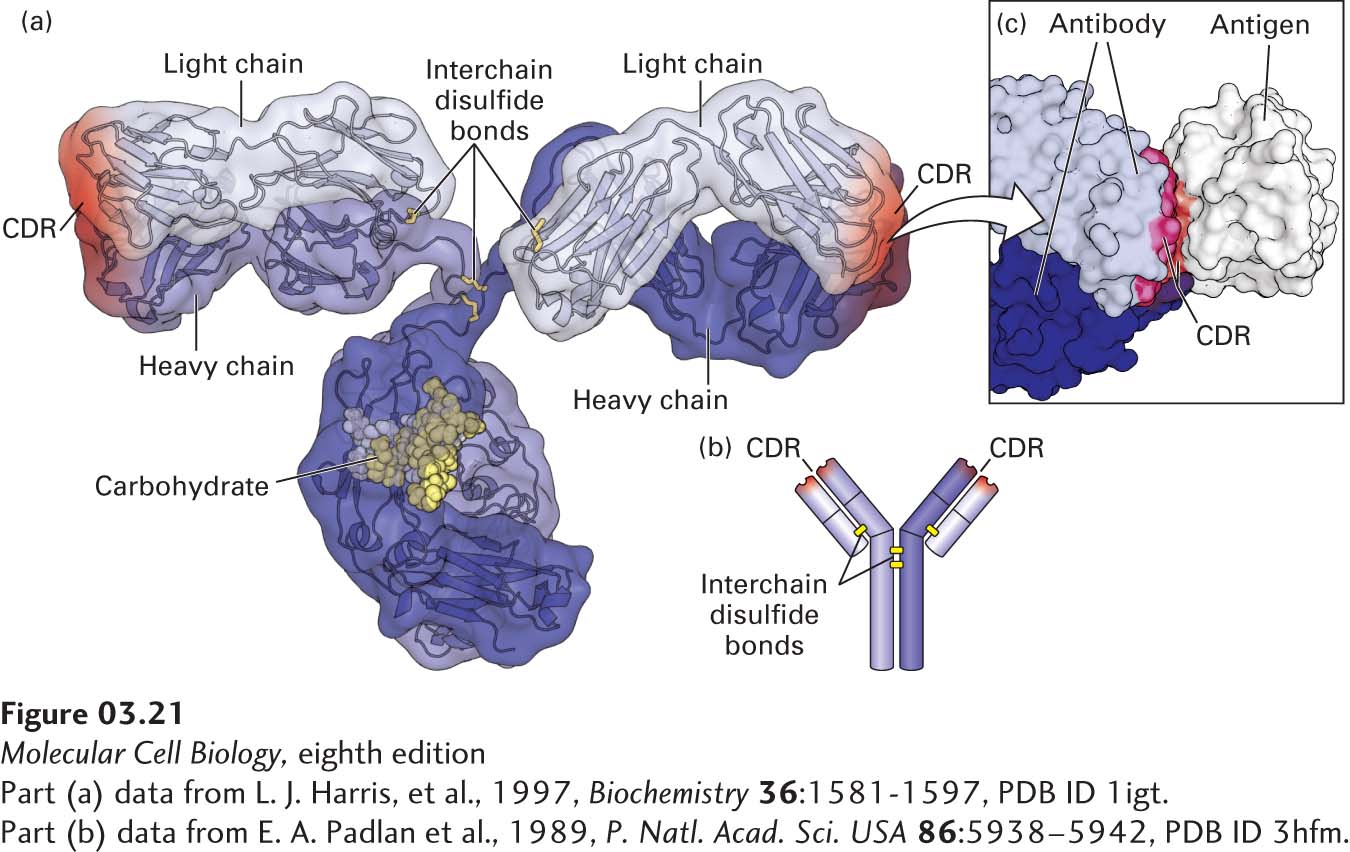
FIGURE 3- 21 Protein- ligand binding of antibodies. (a) Hybrid (surface and ribbon) model of an antibody. Every antibody molecule of the immunoglobulin G (IgG) class consists of two identical heavy chains (medium and dark blue) and two identical light chains (light blue) covalently linked by disulfide bonds (yellow). The complementarity- determining regions (CDRs) that define the antigen- binding sites are represented by red shading. (b) The cartoon shows the overall structure containing the two heavy (longer) and two light (shorter) chains, with yellow bars representing disulfide bonds. (c) The hand- in- glove fit between an antibody and the site to which it binds (epitope) on its target antigen— in this case, chicken egg- white lysozyme. The antibody contacts the antigen with residues from its CDRs.
[Part (a) data from L. J. Harris, et al., 1997, Biochemistry 36:1581- 1597, PDB ID 1igt. Part (c) data from E. A. Padlan et al., 1989, P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:5938– 5942, PDB ID 3hfm.]
[Leave] [Close]