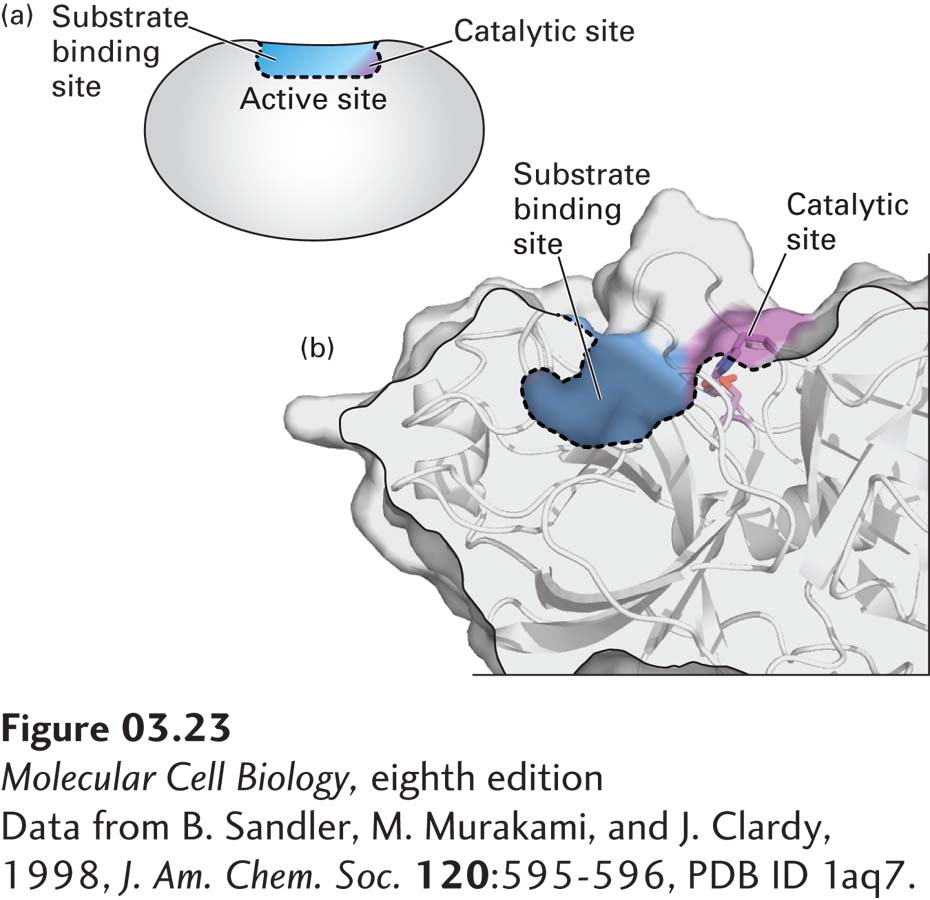
FIGURE 3- e- e- r- p- s- 3- e- e- n-
[Data from B. Sandler, M. Murakami, and J. Clardy, 1998, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120:595-