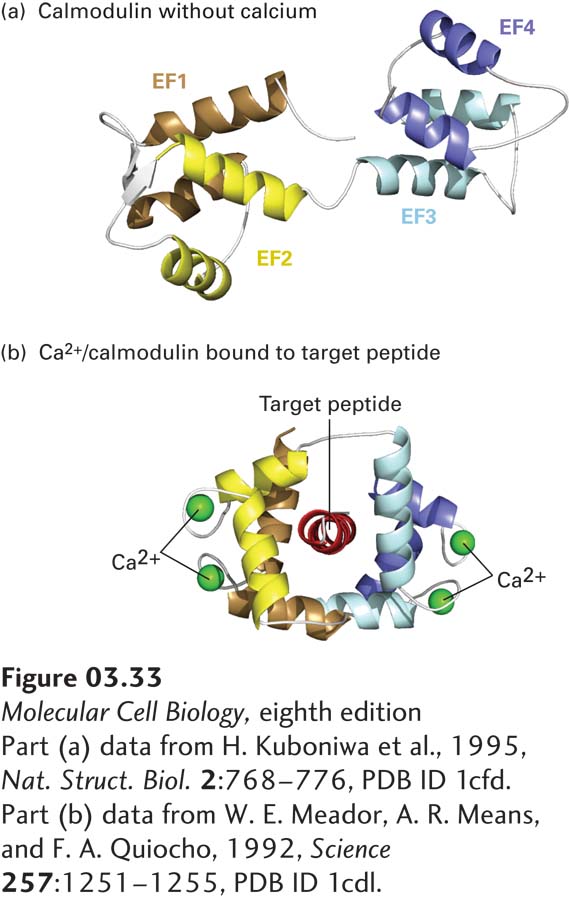
FIGURE 3- x- p- 1- 3- l-
[Part (a) data from H. Kuboniwa et al., 1995, Nat. Struct. Biol. 2:768– 1–