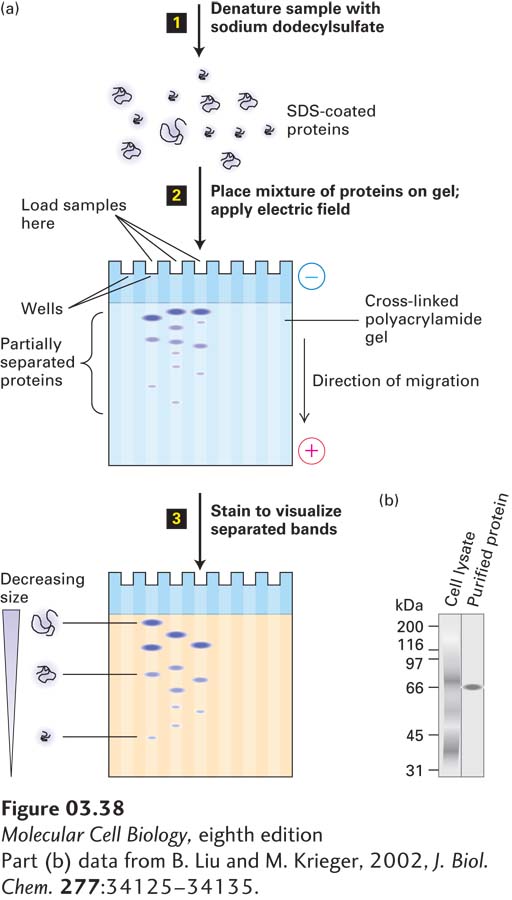
EXPERIMENTAL FIGURE 3- 38 SDS- polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS- PAGE) separates proteins primarily on the basis of their masses. (a) Initial treatment with SDS, a negatively charged detergent, dissociates multimeric proteins and denatures all the polypeptide chains (step 1). During electrophoresis, the SDS- protein complexes migrate through the polyacrylamide gel (step 2). Small complexes are able to move through the pores faster than larger ones. Thus the proteins separate into bands according to their sizes as they migrate. The separated protein bands are visualized by staining with a dye (step 3). (b) Example of SDS- PAGE separation of all the proteins in a whole- cell lysate (detergent- solubilized cells). (Left) The many separate stained proteins appear almost as a continuum. (Right) A single protein purified from the lysate by a single step of antibody- affinity chromatography. The proteins were visualized by staining with a silver- based dye.
[Part (b) data from B. Liu and M. Krieger, 2002, J. Biol. Chem. 277:34125– 34135.]
[Leave] [Close]