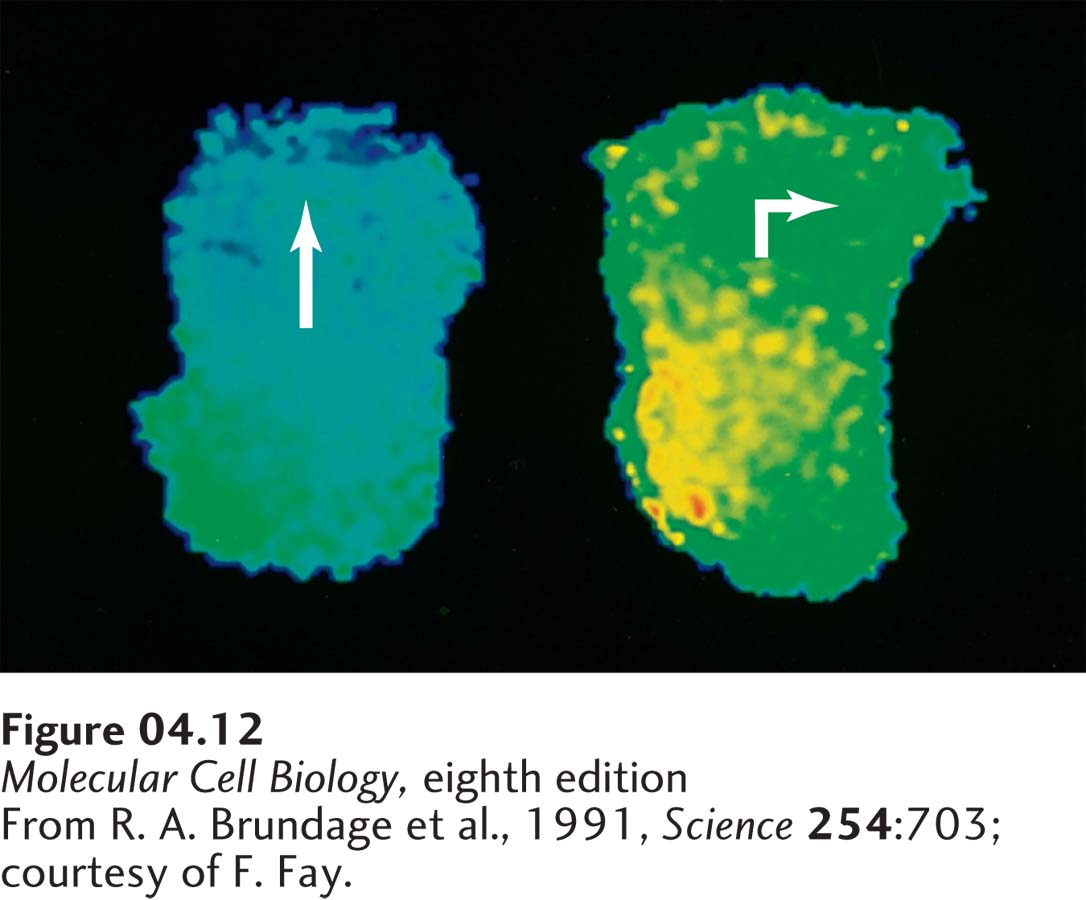
EXPERIMENTAL FIGURE 4- 12 Fura- 2, a Ca2+-sensitive fluorochrome, can be used to monitor the relative concentrations of cytosolic Ca2+ in different regions of live cells. (Left) In a moving leukocyte, a Ca2+ gradient is established. The highest concentrations (green) are at the rear of the cell, where cortical contractions take place, and the lowest concentrations (blue) are at the cell front, where actin undergoes polymerization. (Right) When a pipette filled with chemotactic molecules placed to the side of the cell induces the cell to turn, the Ca2+ concentration momentarily increases throughout the cytoplasm, and a new gradient is established. The gradient is oriented such that the region of lowest Ca2+ (blue) lies in the direction that the cell will turn, whereas a region of high Ca2+ (yellow) always forms at the site that will become the rear of the cell.
[From R. A. Brundage et al., 1991, Science 254:703; courtesy of F. Fay.]
[Leave] [Close]