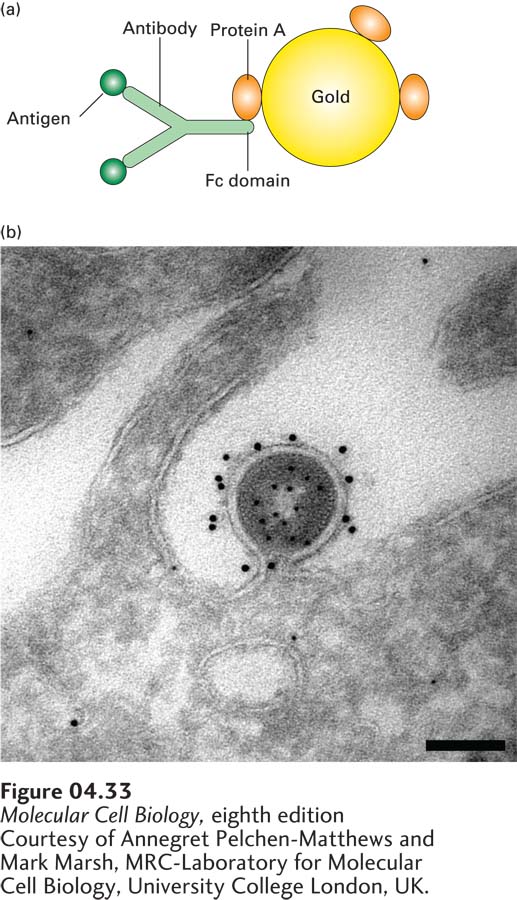
FIGURE 4- 33 Gold particles coated with protein A are used to detect an antibody- bound protein by transmission electron microscopy. (a) First, antibodies are allowed to interact with their specific antigen in a section of fixed tissue. Then the section is treated with electron- dense gold particles coated with protein A from the bacterium S. aureus. Binding of the bound protein A to the Fc domains of the antibody molecules makes the location of the target protein visible in the electron microscope. (b) HIV particle budding from an infected HeLa cell. A cryosection of the specimen was prepared and first incubated with an antibody to capsid protein, then with protein A– coated 5- nm gold particles to localize the internal capsid protein. The unoccupied sites in the protein A were inactivated, and the specimen was incubated with antibody to the membrane- bound Env protein, followed by protein A– coated 10- nm gold particles. The distinct localization of the 5- nm gold labeling the capsid protein and the 10- nm gold labeling the Env protein can be seen. Scale bar is 100 nm.
[Courtesy of Annegret Pelchen- Matthews and Mark Marsh, MRC- Laboratory for Molecular Cell Biology, University College London, UK.]
[Leave] [Close]