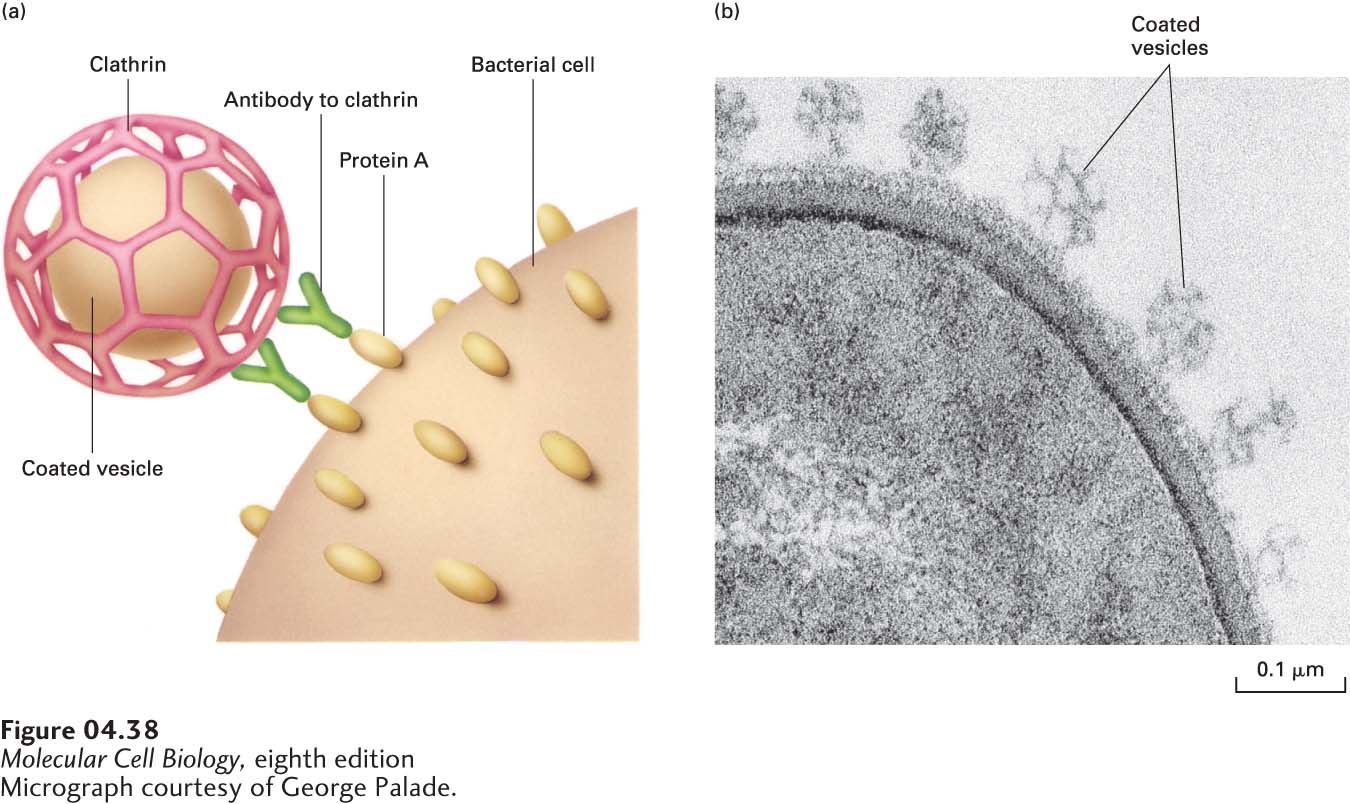
FIGURE 4- 38 Coated vesicles can be purified by binding to an antibody specific for a vesicle surface protein and linkage to bacterial cells. In this example, a suspension of membranes from rat liver is incubated with an antibody specific for clathrin, a protein that coats the outer surface of certain cytosolic vesicles. To this mixture is added a suspension of killed Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, whose surface membrane contains protein A, which binds to the constant (Fc) region of antibodies. (a) Interaction of protein A with antibodies bound to clathrin- coated vesicles links the vesicles to the bacterial cells. The vesicle- bacteria complexes can then be recovered by low- speed centrifugation. (b) A thin- section electron micrograph reveals clathrin- coated vesicles bound to an S. aureus cell. See E. Merisko et al., 1982, J. Cell Biol. 93:846.
[Micrograph courtesy of George Palade.]
[Leave] [Close]