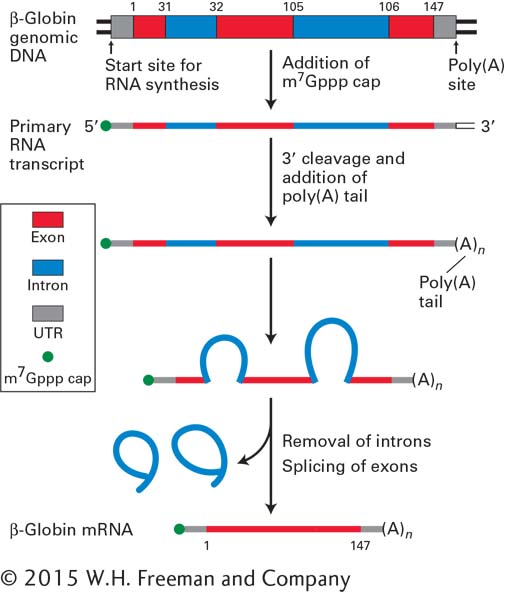
FIGURE 5- n- n- n- 7–