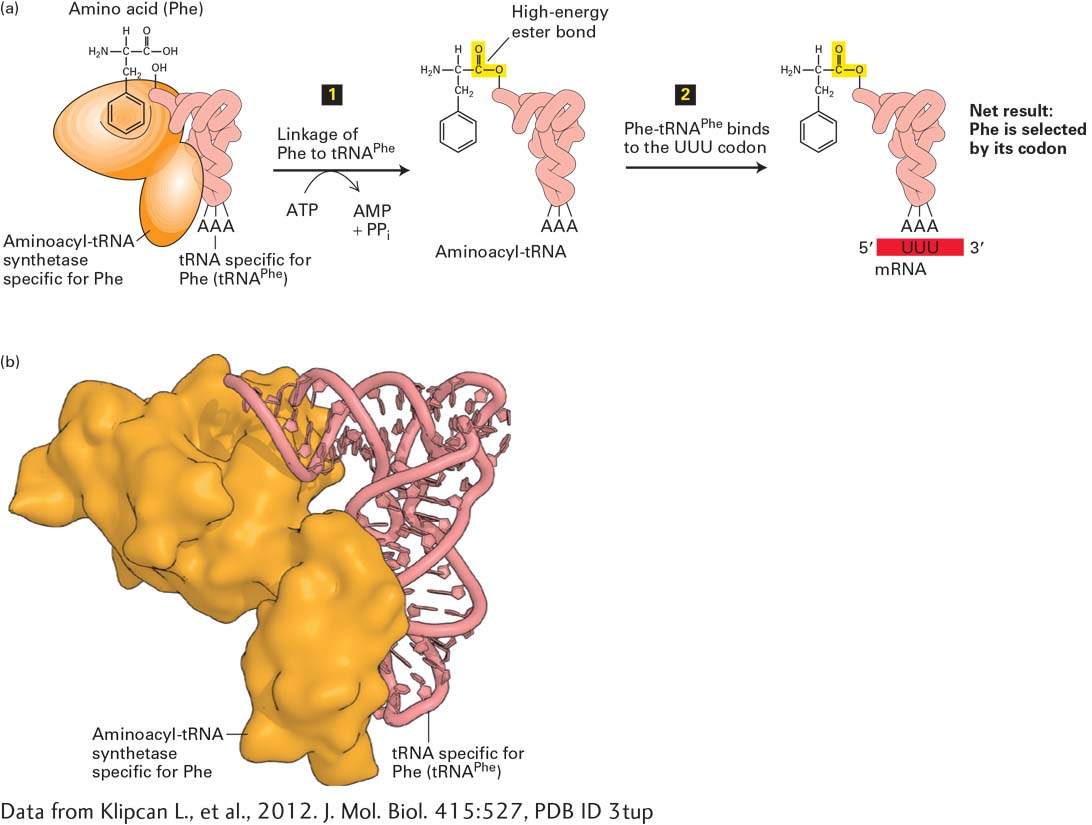
FIGURE 5- l- h- e- e- 5- l-
[Data from Klipcan L., et al., 2012. J. Mol. Biol. 415:527, PDB ID 3tup.]