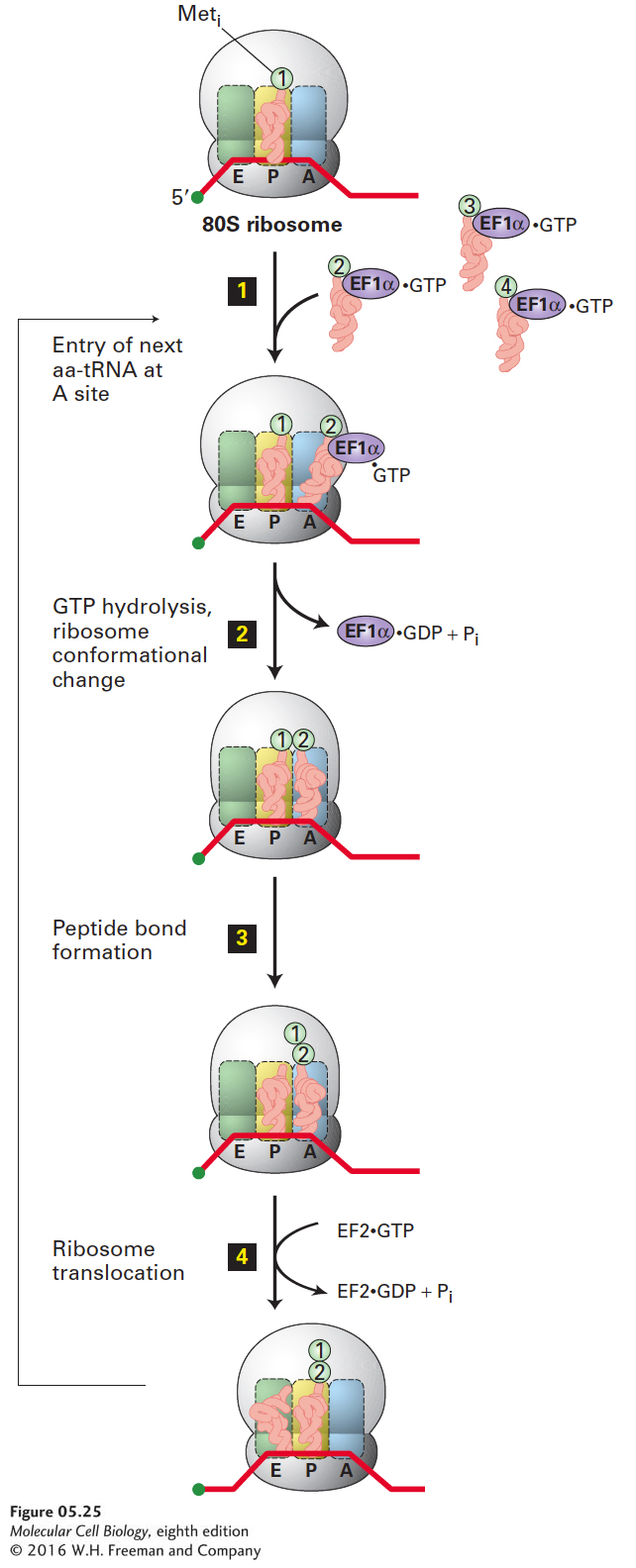
FIGURE 5- 25 Chain elongation in eukaryotes. Once the 80S ribosome with Met- tRNAiMet in the ribosome P site is assembled (top), a ternary complex bearing the second amino acid (aa2) coded by the mRNA binds to the A site (step 1). Following a conformational change in the ribosome induced by hydrolysis of GTP in EF1α·GTP (step 2), the large rRNA catalyzes peptide bond formation between Meti and aa2 (step 3). Hydrolysis of GTP in EF2·GTP causes another conformational change in the ribosome that results in its translocation one codon along the mRNA and shifts the unacylated tRNAiMet to the E site and the tRNA with the bound peptide to the P site (step 4). The cycle can begin again with binding of a ternary complex bearing aa3 to the now open A site. In the second and subsequent elongation cycles, the tRNA at the E site is ejected during step 2 as a result of the conformational change induced by hydrolysis of GTP in EF1α·GTP.
[Leave] [Close]