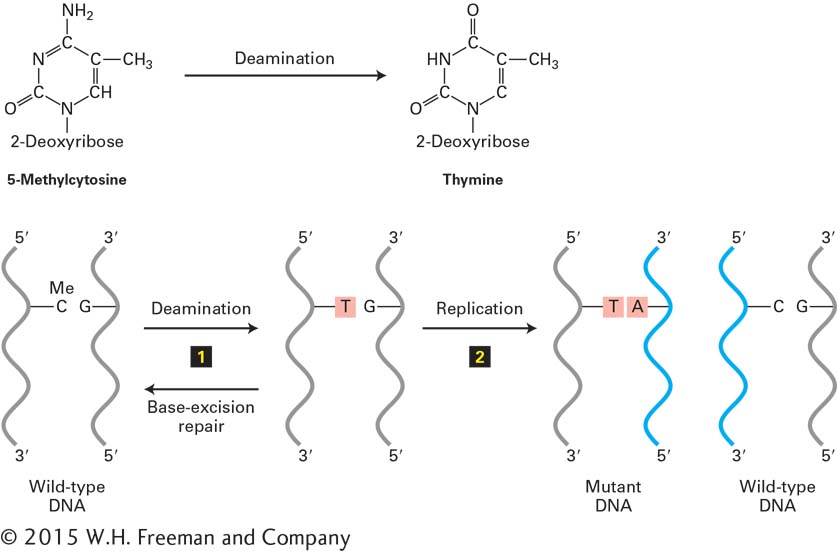
FIGURE 5- 5- n- d-