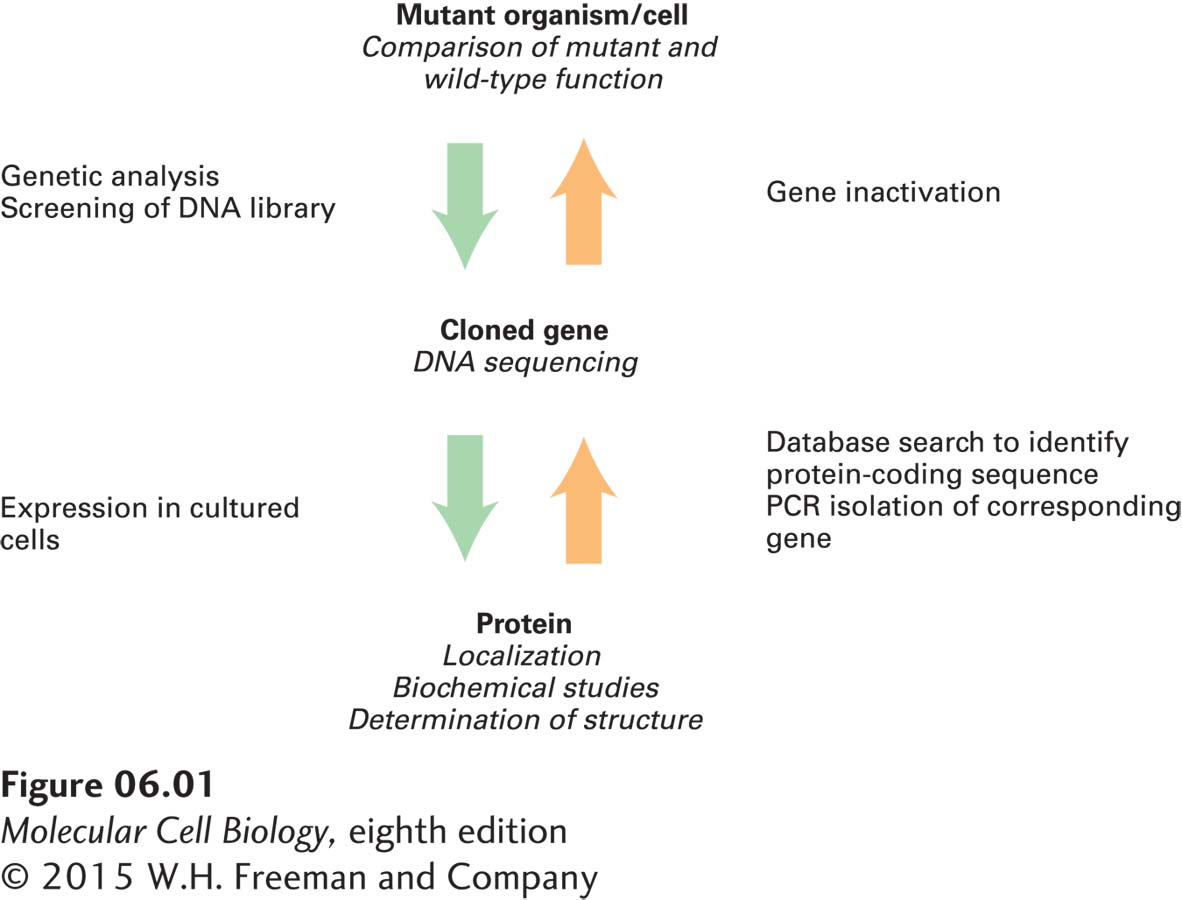
FIGURE 6- 1 Overview of two strategies for relating the function, location, and structure of gene products. A mutant organism is the starting point for the classical genetic strategy (green arrows). The reverse strategy (orange arrows) usually begins with identification of a protein- coding sequence by analysis of genomic sequence databases. In both strategies, the actual gene is isolated either from a DNA library or by specific amplification of the gene sequence from genomic DNA. Once a cloned gene is isolated, it can be used to produce the encoded protein in bacterial or eukaryotic expression systems. Alternatively, a cloned gene can be inactivated by one of various techniques and used to generate mutant cells or organisms.
[Leave] [Close]