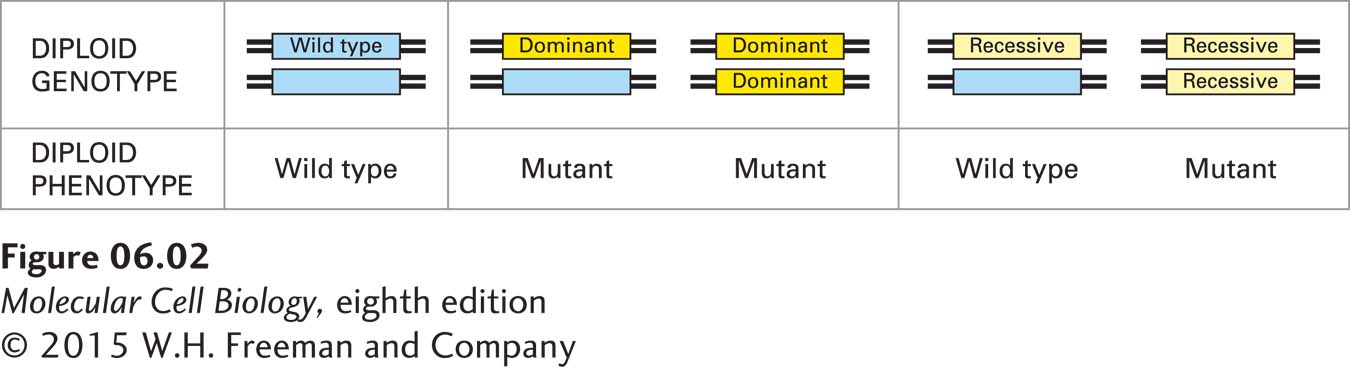
FIGURE 6- 2 Effects of dominant and recessive mutant alleles on phenotype in diploid organisms. A single copy of a dominant mutant allele is sufficient to produce a mutant phenotype, whereas both copies of a recessive mutant allele must be present to cause a mutant phenotype. Recessive mutations usually cause a loss of function; dominant mutations usually cause a gain of function or an altered function.
[Leave] [Close]