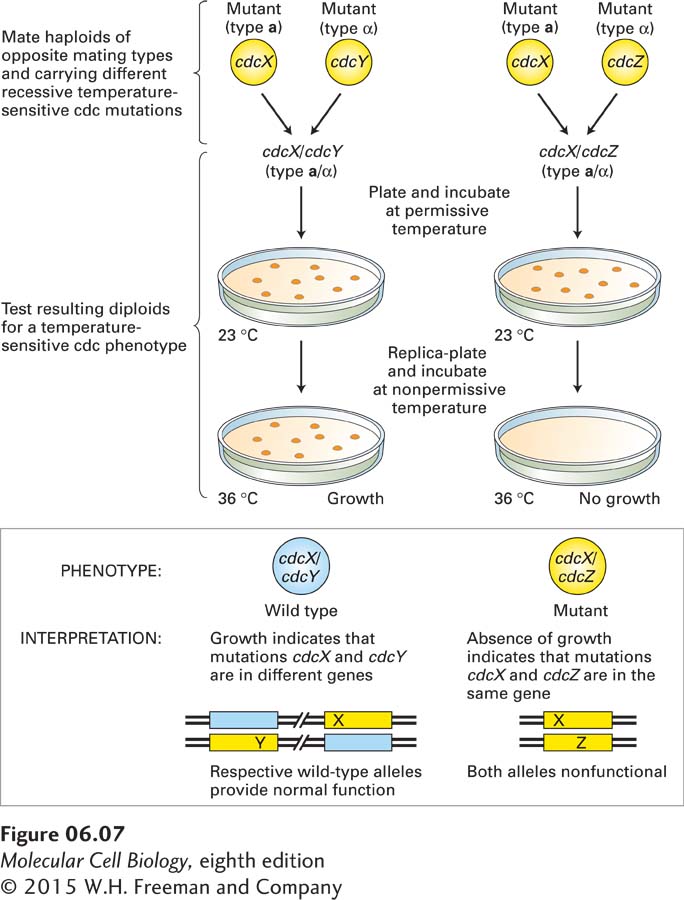
EXPERIMENTAL FIGURE 6- 7 Complementation analysis determines whether recessive mutations are in the same or different genes. Complementation tests in yeast are performed by mating haploid a and α cells carrying different recessive mutations to produce diploid cells. In the analysis of cdc mutations, pairs of different haploid temperature- sensitive cdc strains were systematically mated and the resulting diploids tested for growth at the permissive and nonpermissive temperatures. In this hypothetical example, the cdcX and cdcY mutants complement each other, and thus have mutations in different genes, whereas the cdcX and cdcZ mutants have mutations in the same gene.
[Leave] [Close]